Prognostic factors of Takotsubo cardiomyopathy: a systematic review
- PMID: 34374223
- PMCID: PMC8497208
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.13531
Prognostic factors of Takotsubo cardiomyopathy: a systematic review
Abstract
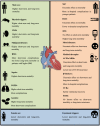
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy (TCM), characterized by reversible ventricular dysfunction, has similar mortality to acute coronary syndrome. With the growing interest in the diagnosis of and interventions for TCM, many risk factors had been found to affect the prognosis of TCM patients, such as age, sex, and pre-existing diseases. Because of the incomplete understanding of the pathophysiologic mechanism in TCM, evidence-based medical therapy for this condition is lacking. Early intervention on risk factors may improve the outcomes of TCM. In this review, we sought to provide up-to-date evidence on risk factors and medical therapies that affect TCM outcome. We found that male sex, physical triggers, and certain comorbidities such as chronic kidney disease, malignant disease, higher body mass index, sepsis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and anaemia were associated with poor TCM prognosis. In contrast, race, hyperlipidaemia, diabetes mellitus, and mood disorders were not clearly associated with TCM prognosis. We also reviewed the effect of medical therapies on TCM outcome, including angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers, β-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and statins. The evidence that these medications confer a survival benefit on TCM patients is limited. Understanding these prognostic factors could help develop risk-stratification tools for TCM and establish effective prevention and interventions for this not-so-benign condition. Further multicentre clinical studies with large samples and meta-analyses of findings from previous studies are needed to address the inconsistent findings among the many potential risk factors for TCM.
Keywords: Prognosis; Risk factors; Takotsubo cardiomyopathy; Treatment.
© 2021 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Music interventions for improving psychological and physical outcomes in people with cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 12;10(10):CD006911. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006911.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34637527 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Takotsubo syndrome linked to paroxysmal sympathetic hyperactivity as a postoperative complication after brain tumor removal: a case report and literature review.Childs Nerv Syst. 2024 Aug;40(8):2573-2579. doi: 10.1007/s00381-024-06316-9. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Childs Nerv Syst. 2024. PMID: 38383868 Review.
-
Temperature and repeated catecholamine surges modulate regional wall motion abnormalities in a rodent takotsubo syndrome model.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 31;15(1):3876. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88410-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39890974 Free PMC article.
-
Takotsubo Syndrome in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review.CJC Open. 2024 Mar 13;6(6):818-825. doi: 10.1016/j.cjco.2024.03.004. eCollection 2024 Jun. CJC Open. 2024. PMID: 39022174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychosocial and clinical characteristics in Takotsubo syndrome.Biol Sex Differ. 2025 Jun 16;16(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13293-025-00729-0. Biol Sex Differ. 2025. PMID: 40524204 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Multifaceted Problems Associated with Dysrhythmia.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 23;25(1):263. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010263. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203440 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Isogai T, Yoshikawa T, Ueda T, Yamaguchi T, Imori Y, Maekawa Y, Sakata K, Murakami T, Mochizuki H, Arao K, Kimura A, Nagao K, Yamamoto T, Takayama M. Apical Takotsubo syndrome versus anterior acute myocardial infarction: findings from the Tokyo Cardiovascular Care Unit network registry. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care 2019; 8: 86–95. - PubMed
-
- Ono R, Falcão LM. Takotsubo cardiomyopathy systematic review: pathophysiologic process, clinical presentation and diagnostic approach to Takotsubo cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiol 2016; 209: 196–205. - PubMed
-
- Akashi YJ, Nakazawa K, Sakakibara M, Miyake F, Musha H, Sasaka K. 123I‐MIBG myocardial scintigraphy in patients with “takotsubo” cardiomyopathy. J Nucl Med 2004; 45: 1121–1127. - PubMed
-
- Bybee KA, Prasad A, Barsness GW, Lerman A, Jaffe AS, Murphy JG, Wright RS, Rihal CS. Clinical characteristics and thrombolysis in myocardial infarction frame counts in women with transient left ventricular apical ballooning syndrome. Am J Cardiol 2004; 94: 343–346. - PubMed
-
- Ito K, Sugihara H, Katoh S, Azuma A, Nakagawa M. Assessment of Takotsubo (ampulla) cardiomyopathy using 99mTc‐tetrofosmin myocardial SPECT—comparison with acute coronary syndrome. Ann Nucl Med 2003; 17: 115–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

