EGFR-mutated stage IV non-small cell lung cancer: What is the role of radiotherapy combined with TKI?
- PMID: 34374490
- PMCID: PMC8446557
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.4192
EGFR-mutated stage IV non-small cell lung cancer: What is the role of radiotherapy combined with TKI?
Abstract
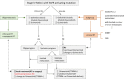
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death globally and poses a considerable threat to public health. Asia has the highest prevalence of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Despite the reasonable response and prolonged survival associated with EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy, the acquisition of resistance to TKIs remains a major challenge. Additionally, patients with EGFR mutations are at a substantially higher risk of brain metastasis compared with those harboring wild-type EGFR. The role of radiotherapy (RT) in EGFR-mutated (EGFRm) stage IV NSCLC requires clarification, especially with the advent of next-generation TKIs, which are more potent and exhibit greater central nervous system activity. In particular, the feasible application of RT, including the timing, site, dose, fraction, and combination with TKI, merits further investigation. This review focuses on these key issues, and provides a flow diagram with proposed treatment options for metastatic EGFRm NSCLC, aiming to provide guidance for clinical practice.
Keywords: EGFR mutation; TKI; radiotherapy.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors made no disclosures.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Concurrent EGFR-TKI and Thoracic Radiotherapy as First-Line Treatment for Stage IV Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring EGFR Active Mutations.Oncologist. 2019 Aug;24(8):1031-e612. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0285. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 31040256 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical outcome of tyrosine kinase inhibitors alone or combined with radiotherapy for brain metastases from epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutant non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 21;8(8):13304-13311. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14515. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28076323 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the efficacies of first-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors for brain metastasis in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations.BMC Cancer. 2018 Oct 22;18(1):1012. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4911-7. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30348116 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing the sequencing of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Lung Cancer. 2019 Nov;137:113-122. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.09.017. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31568888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of Brain Metastases of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 8;22(2):593. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020593. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33435596 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Survival benefit of thoracic radiotherapy plus EGFR-TKIs in patients with non-oligometastatic advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a single-center retrospective study.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2023 Mar 21;15:17588359231161411. doi: 10.1177/17588359231161411. eCollection 2023. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36970112 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an adenosquamous carcinoma histopathology - selective lung metastasis model.Biol Open. 2022 Dec 15;11(12):bio059623. doi: 10.1242/bio.059623. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Biol Open. 2022. PMID: 36355420 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing Osimertinib for NSCLC: Targeting Resistance and Exploring Combination Therapeutics.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jan 29;17(3):459. doi: 10.3390/cancers17030459. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39941826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploration of radiotherapy strategy for brain metastasis patients with driver gene positivity in lung cancer.J Cancer. 2024 Feb 12;15(7):1994-2002. doi: 10.7150/jca.91875. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38434971 Free PMC article.
-
Early stereotactic body radiation therapy improves progression-free survival of first-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutated lung cancer: an observational cohort study.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2024 Nov 4;16:17588359241290133. doi: 10.1177/17588359241290133. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39502405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394‐424. - PubMed
-
- Cho BC, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, et al. Osimertinib versus standard of care EGFR TKI as first‐line treatment in patients with EGFRm advanced NSCLC: FLAURA Asian subset. J Thorac Oncol. 2019;14(1):99‐106. - PubMed
-
- Iuchi T, Shingyoji M, Itakura M, et al. Frequency of brain metastases in non‐small‐cell lung cancer, and their association with epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. Int J Clin Oncol. 2015;20(4):674‐679. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

