Three-dimensional MR Elastography Depicts Liver Inflammation, Fibrosis, and Portal Hypertension in Chronic Hepatitis B or C
- PMID: 34374594
- PMCID: PMC8475654
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2021202804
Three-dimensional MR Elastography Depicts Liver Inflammation, Fibrosis, and Portal Hypertension in Chronic Hepatitis B or C
Abstract
Background The value of measuring mechanical properties to categorize various pathophysiologic states of the liver is as yet undetermined in chronic hepatitis B (CHB) or C (CHC). Purpose To evaluate multiparametric three-dimensional (3D) MR elastography as a means of detecting early necroinflammation, distinguishing necroinflammation from fibrosis, and gauging the severity of portal hypertension (PH) in CHB or CHC. Materials and Methods From January 2015 to September 2019, participants with CHB or CHC were prospectively enrolled from a single institution and were divided into two groups: those with liver biopsy and no evidence of PH (group 1) and those with PH and a hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) measurement (group 2). For group 3, healthy volunteers were separately recruited from a nearby community. Multiple viscoelastic parameters (shear stiffness [SS], storage modulus, loss modulus, and damping ratio [DR]) were determined at 3D MR elastography at 60 Hz, and multivariable logistic or linear regression analysis was used to assess associations of mechanical parameters with histologic scores and HVPG. Results A total of 155 participants (median age, 41 years [interquartile range, 32-48 years]; 85 women) were in group 1 (training set: n = 78, validation set: n = 77), 85 participants (median age, 57 years [interquartile range, 43-61 years]; 51 women) in group 2, and 60 healthy volunteers (median age, 49 years [interquartile range, 27-64 years]; 38 men) in group 3. The liver DR was higher in participants with necroinflammation (DR, 0.13 ± 0.03) versus those without (at liver fibrosis stage F0) (DR, 0.10 ± 0.02; P < .001). Liver DR and SS together performed well in the diagnosis of necroinflammation (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve [AUC], 0.88 [95% CI: 0.79, 0.96]) and the scoring of moderate to severe activity (AUC, 0.88 [95% CI: 0.81, 0.95]) in the validation data set. Liver DR (regression coefficient [β] = -30.3 [95% CI: -58.0, -2.5]; P = .03) and splenic SS (β = 2.3 [95% CI: 1.7, 2.9]; P < .001) were independently associated with HVPG. Conclusion Three-dimensional MR elastography may detect early necroinflammation, distinguish necroinflammation from liver fibrosis, and correlate with hepatic venous pressure gradient in chronic hepatitis B and C. © RSNA, 2021 Online supplemental material is available for this article. See also the editorial by Reeder in this issue.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

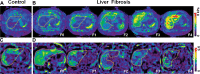
![Boxplots show liver shear stiffness (SS) and damping ratio (DR)
determinations in participants with liver fibrosis (LF), assessed with
three-dimensional MR elastography. The lower and upper borders of boxes
correspond to the first and third quartiles (the 25th and 75th percentiles).
The midline of boxes indicate medians. The lower and upper whiskers
correspond to the 5th and 95th percentiles, respectively. Dots beyond the
end of the whiskers indicate outliers. (A) SS increased according to LF
stage (all P < .001; adjusted α = .005). (B) DR was consistent
across stages F0–F2, with declines at stages F3 and F4 (F0 vs F3 [P =
.002], F0 vs F4 [P < .001], F2 vs F4 [P < .001], and F2 vs F3
[P = .003]; adjusted α = .005).](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/26f6/8475654/e7bd2976d958/radiol.2021202804.fig3.gif)
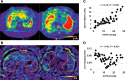
![Boxplots show liver shear stiffness (SS) and damping ratio (DR)
determinations in participants with liver fibrosis (LF) and
necroinflammation, assessed with three-dimensional MR elastography. The
lower and upper borders of the boxes correspond to the first and third
quartiles (the 25th and 75th percentiles). The midline indicates the median.
The lower and upper whiskers correspond to the smallest and largest values,
respectively, no further than 1.5 box lengths from the median. Dots beyond
the end of the whiskers indicate outliers. (A, B) Boxplots illustrate liver
SS with (A) the A0 versus A1–A3 activity score and (B) A0–A1
versus A2–A3 activity score at each LF stage (P = .04 at A0 [vs
A1–A3] for stage F0). (C, D) Boxplots illustrate liver DR with (C)
the A0 versus A1–A3 activity score and (D) A0–A1 versus
A2–A3 activity score at each LF stage (significance at stage F0 in A0
vs A1–A3 [P < .001] and A0–A1 vs A2–A3 [P =
.007] and stage F1 in A0–A1 vs A2–A3 [P = .001]).](https://cdn.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/blobs/26f6/8475654/6c4758981d1e/radiol.2021202804.fig4.gif)
Comment in
-
Emergence of 3D MR Elastography-based Quantitative Markers for Diffuse Liver Disease.Radiology. 2021 Oct;301(1):163-165. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021211444. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Radiology. 2021. PMID: 34374596 No abstract available.
-
Three-dimensional MR Elastography in Distinguishing Necroinflammation from Liver Fibrosis.Radiology. 2022 Aug;304(2):E43. doi: 10.1148/radiol.212154. Epub 2022 May 17. Radiology. 2022. PMID: 35579520 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Guidelines for the Prevention, Care and Treatment of Persons with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection . Geneva, Switzerland: : World Health Organization, 2015. . - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Guidelines for the Screening Care and Treatment of Persons with Chronic Hepatitis C Infection. Updated Version . Geneva, Switzerland: : World Health Organization, 2016. . - PubMed
-
- Shi Y , Xia F , Li QJ , et al. . Magnetic resonance elastography for the evaluation of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B and C by using both gradient-recalled echo and spin-echo echo planar imaging: a prospective study . Am J Gastroenterol 2016. ; 111 ( 6 ): 823 – 833 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

