Long noncoding RNA RP11-70C1.3 confers chemoresistance of breast cancer cells through miR-6736-3p/NRP-1 axis
- PMID: 34374639
- PMCID: PMC8860307
- DOI: 10.17305/bjbms.2021.5803
Long noncoding RNA RP11-70C1.3 confers chemoresistance of breast cancer cells through miR-6736-3p/NRP-1 axis
Abstract
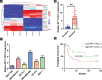
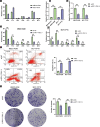
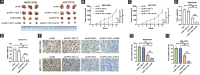
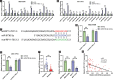
Chemoresistance remains a major obstacle for improving the clinical outcome of patients with breast cancer. Recently, long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been implicated in breast cancer chemoresistance. However, the function and underlying mechanism are still largely unknown. Using lncRNA microarray, we identified 122 upregulated and 475 downregulated lncRNAs that might be related to the breast cancer chemoresistance. Among them, RP11-70C1.3 was one of the most highly expressed lncRNAs. In breast cancer patients, high RP11-70C1.3 expression predicted poor prognosis. Knockdown of RP11-70C1.3 inhibited the multidrug resistance of breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Further investigations revealed that RP11-70C1.3 functioned as a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) for miR-6736-3p to increase NRP-1 expression. Notably, the rescue experiments showed that both miR-6736-3p inhibitor and NRP-1 overexpression could partly reverse the suppressive influence of RP11-70C1.3 knockdown on breast cancer chemoresistance. In conclusion, our study indicated that lncRNA RP11-70C1.3 regulated NRP-1 expression by sponging miR-6736-3p to confer chemoresistance of breast cancer cells. RP11-70C1.3 might be a potential therapeutic target in enhancing the clinical efficacy of chemotherapy in breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA RP11-283G6.5 confines breast cancer development through modulating miR-188-3p/TMED3/Wnt/β-catenin signalling.RNA Biol. 2021 Oct 15;18(sup1):287-302. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1941608. Epub 2021 Jul 27. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 34130584 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA NEAT1 promotes the Taxol resistance of breast cancer via sponging the miR-23a-3p-FOXA1 axis.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021 Aug 31;53(9):1198-1206. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmab098. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021. PMID: 34327529
-
LncRNA RP11-79H23.3 Functions as a Competing Endogenous RNA to Regulate PTEN Expression through Sponging hsa-miR-107 in the Development of Bladder Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 26;19(9):2531. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092531. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30149689 Free PMC article.
-
miR-495-3p as a promising tumor suppressor in human cancers.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Aug;248:154610. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154610. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37307621 Review.
-
Breast Cancer Chemoresistance: Insights into the Regulatory Role of lncRNA.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 2;24(21):15897. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115897. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958880 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long noncoding RNA PPP1R14B-AS1 imitates microRNA-134-3p to facilitate breast cancer progression by upregulating LIM and SH3 protein 1.Oncol Res. 2022 Aug 31;29(4):251-262. doi: 10.32604/or.2022.03582. eCollection 2021. Oncol Res. 2022. PMID: 37303940 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between LncRNAs and microRNAs in Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 30;24(9):8095. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098095. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 promotes chemoresistance in triple-negative breast cancer through the miR-524-5p/RBM39 axis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Jan;480(1):371-384. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04908-8. Epub 2024 Mar 12. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 38472681
-
Knockdown of lncRNA FOXD2-AS1 Inhibits Proliferation, Migration, and Drug Resistance of Breast Cancer Cells.Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Nov 27;2021:9674761. doi: 10.1155/2021/9674761. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Sep 27;2023:9854591. doi: 10.1155/2023/9854591. PMID: 34873418 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020:GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660. - PubMed
-
- Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(19):10869–74. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.191367098. - PMC - PubMed
-
- DeSantis CE, Ma J, Gaudet MM, Newman LA, Miller KD, Sauer AG, et al. Breast cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(6):438–51. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21583. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhary B, Khaled YS, Ammori BJ, Elkord E. Neuropilin 1:Function and therapeutic potential in cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2014;63(2):81–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-013-1500-0. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW, Bartel DP. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife. 2015;4:e05005. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.05005. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

