Hedgehog interacting protein-expressing lung fibroblasts suppress lymphocytic inflammation in mice
- PMID: 34375314
- PMCID: PMC8492352
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.144575
Hedgehog interacting protein-expressing lung fibroblasts suppress lymphocytic inflammation in mice
Abstract
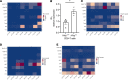
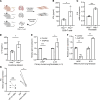
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is mainly caused by cigarette smoking and characterized by chronic inflammation in vulnerable individuals. However, it is unknown how genetic factors may shape chronic inflammation in COPD. To understand how hedgehog interacting protein, encoded by HHIP gene identified in the genome-wide association study in COPD, plays a role in inflammation, we utilized Hhip+/- mice that present persistent inflammation and emphysema upon aging similar to that observed in human COPD. By performing single-cell RNA sequencing of the whole lung from mice at different ages, we found that Hhip+/- mice developed a cytotoxic immune response with a specific increase in killer cell lectin-like receptor G1-positive CD8+ T cells with upregulated Ifnγ expression recapitulating human COPD. Hhip expression was restricted to a lung fibroblast subpopulation that had increased interaction with CD8+ T lymphocytes in Hhip+/- compared with Hhip+/+ during aging. Hhip-expressing lung fibroblasts had upregulated IL-18 pathway genes in Hhip+/- lung fibroblasts, which was sufficient to drive increased levels of IFN-γ in CD8+ T cells ex vivo. Our finding provides insight into how a common genetic variation contributes to the amplified lymphocytic inflammation in COPD.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00608764.
Keywords: COPD; Inflammation; Mouse models; Pulmonology.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Metabolomic profiling in a Hedgehog Interacting Protein (Hhip) murine model of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Sci Rep. 2017 May 31;7(1):2504. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02701-4. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28566717 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease genetic determinant that regulates HHIP.Hum Mol Genet. 2012 Mar 15;21(6):1325-35. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr569. Epub 2011 Dec 2. Hum Mol Genet. 2012. PMID: 22140090 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog interacting protein (HHIP) represses airway remodeling and metabolic reprogramming in COPD-derived airway smooth muscle cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 27;11(1):9074. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88434-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33907231 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog pathway and its inhibitors in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Dec;240:108295. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108295. Epub 2022 Oct 1. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 36191777 Review.
-
[Recent progress in genetic background of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)].Nihon Rinsho. 2016 May;74(5):733-42. Nihon Rinsho. 2016. PMID: 27254938 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Inherent immunity and adaptive immunity: Mechanism and role in AECOPD.Innate Immun. 2025 Jan-Dec;31:17534259251322612. doi: 10.1177/17534259251322612. Innate Immun. 2025. PMID: 40017227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: understanding the pathobiology and heterogeneity of a complex disorder.Lancet Respir Med. 2022 May;10(5):485-496. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00510-5. Epub 2022 Apr 12. Lancet Respir Med. 2022. PMID: 35427534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in acute COPD exacerbation: clarifying specific immune mechanisms of infectious and noninfectious factors.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2025 Jan-Dec;19:17534666241308408. doi: 10.1177/17534666241308408. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2025. PMID: 40098281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Mechanism by Which Hedgehog Interacting Protein (HHIP) in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Regulate the Secretion of Inflammatory Factors Through the JAK1/STAT3 Pathway Affecting Prostate Cancer Stemness.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Nov 11;17:8659-8680. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S472124. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39553307 Free PMC article.
-
The Microbiota and Evolution of Obesity.Endocr Rev. 2025 Mar 11;46(2):300-316. doi: 10.1210/endrev/bnae033. Endocr Rev. 2025. PMID: 39673174 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

