Using the Goldilocks Principle to model coral ecosystem engineering
- PMID: 34375552
- PMCID: PMC8354746
- DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2021.1260
Using the Goldilocks Principle to model coral ecosystem engineering
Abstract
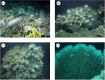
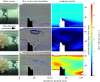
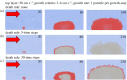
The occurrence and proliferation of reef-forming corals is of vast importance in terms of the biodiversity they support and the ecosystem services they provide. The complex three-dimensional structures engineered by corals are comprised of both live and dead coral, and the function, growth and stability of these systems will depend on the ratio of both. To model how the ratio of live : dead coral may change, the 'Goldilocks Principle' can be used, where organisms will only flourish if conditions are 'just right'. With data from particle imaging velocimetry and numerical smooth particle hydrodynamic modelling with two simple rules, we demonstrate how this principle can be applied to a model reef system, and how corals are effectively optimizing their own local flow requirements through habitat engineering. Building on advances here, these approaches can be used in conjunction with numerical modelling to investigate the growth and mortality of biodiversity supporting framework in present-day and future coral reef structures.
Keywords: Goldilocks Principle; Lophelia pertusa; coral; flow velocity; particle image velocimetry; smoothed-particle hydrodynamics modelling.
Figures


References
-
- Henry L-A, Navas JM, Hennige SJ, Wicks LC, Vad J, Murray Roberts J. 2013Cold-water coral reef habitats benefit recreationally valuable sharks. Biol. Conserv. 161, 67-70. ( 10.1016/j.biocon.2013.03.002) - DOI
-
- D'Onghia G, Maiorano P, Carlucci R, Capezzuto F, Carluccio A, Tursi A, Sion L. 2012Comparing deep-sea fish fauna between coral and non-coral ‘megahabitats’ in the Santa Maria di Leuca cold-water coral province (Mediterranean Sea). PLoS ONE 7, e44509. ( 10.1371/journal.pone.0044509) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buhl-Mortensen L, Vanreusel A, Gooday AJ, Levin LA, Priede IG, Buhl-Mortensen P, Gheerardyn H, King NJ, Raes M. 2010Biological structures as a source of habitat heterogeneity and biodiversity on the deep ocean margins. Mar. Ecol. 31, 21-50. ( 10.1111/j.1439-0485.2010.00359.x) - DOI
-
- Rossi S, Bramanti L, Gori A, Orejas C. 2017Marine animal forests: the ecology of benthic biodiversity hotspots. Berlin, Germany: Springer.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
