Multi-locus genome-wide association studies for five yield-related traits in rice
- PMID: 34376143
- PMCID: PMC8353822
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-021-03146-8
Multi-locus genome-wide association studies for five yield-related traits in rice
Abstract
Background: Improving the overall production of rice with high quality is a major target of breeders. Mining potential yield-related loci have been geared towards developing efficient rice breeding strategies. In this study, one single-locus genome-wide association studies (SL-GWAS) method (MLM) in conjunction with five multi-locus genome-wide association studies (ML-GWAS) approaches (mrMLM, FASTmrMLM, pLARmEB, pKWmEB, and ISIS EM-BLASSO) were conducted in a panel consisting of 529 rice core varieties with 607,201 SNPs.
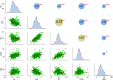
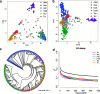
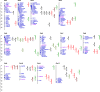
Results: A total of 152, 106, 12, 111, and 64 SNPs were detected by the MLM model associated with the five yield-related traits, namely grain length (GL), grain width (GW), grain thickness (GT), thousand-grain weight (TGW), and yield per plant (YPP), respectively. Furthermore, 74 significant quantitative trait nucleotides (QTNs) were presented across at least two ML-GWAS methods to be associated with the above five traits successively. Finally, 20 common QTNs were simultaneously discovered by both SL-GWAS and ML-GWAS methods. Based on genome annotation, gene expression analysis, and previous studies, two candidate key genes (LOC_Os09g02830 and LOC_Os07g31450) were characterized to affect GW and TGW, separately.
Conclusions: These outcomes will provide an indication for breeding high-yielding rice varieties in the immediate future.
Keywords: ML-GWAS; MLM; Oryza sativa; QTNs; Yield.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests
Figures

References
-
- Challinor AJ, Watson J, Lobell DB, Howden SM, Smith DR, Chhetri N. A meta-analysis of crop yield under climate change and adaptation. Nat Clim Chang. 2014;4(4):287–291. doi: 10.1038/nclimate2153. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

