Endoscopic and fluoroscopic-guided closure of the eustachian tube using a biliary cytology brush and liquid embolic agent for a persistent CSF leak after schwannoma resection
- PMID: 34376411
- PMCID: PMC8356153
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2021-241861
Endoscopic and fluoroscopic-guided closure of the eustachian tube using a biliary cytology brush and liquid embolic agent for a persistent CSF leak after schwannoma resection
Abstract
Vestibular schwannoma is a known cause of progressive sensorineural hearing loss. Treatment options include observation, radiation therapy and surgical resection. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) fistula is a known postsurgical complication that can lead to CSF otorrhoea, rhinorrhoea or CSF leakage from the surgical wound. We present a case report of a patient who underwent vestibular schwannoma resection and postoperatively developed CSF rhinorrhoea, which was refractory to multiple attempts at surgical repair. This was successfully treated under endoscopic and fluoroscopic guidance using a biliary cytology brush to disrupt the surface of the eustachian tube followed by injection of n-Butyl cyanoacrylate.
Keywords: ear; interventional radiology; nose and throat/otolaryngology.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2021. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
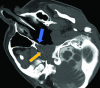
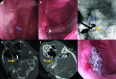
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
