Classic biphasic pulmonary blastoma (CBPB): a rare primary pulmonary malignancy
- PMID: 34376421
- PMCID: PMC8356168
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2021-244151
Classic biphasic pulmonary blastoma (CBPB): a rare primary pulmonary malignancy
Abstract
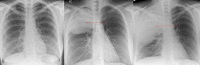
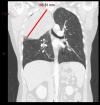
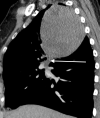
Classic biphasic pulmonary blastoma (CBPB) is a very rare primary pulmonary malignancy with distinctive clinical and pathological features. Usually CBPB presents with either non specific symptoms or is diagnosed incidentally. Histologically CBPB is composed of a mixture of malignant epithelial and stromal cells resembling fetal lung tissue. Surgical resection is the mainstay of treatment with further chemotherapy or radiotherapy on a case-by-case basis. However, due to its rarity, no definite treatment guidelines are available. CBPB overall has a very poor prognosis with a 5-year survival rate of only 15%. Our patient presented with cough and haemoptysis. Her chest radiograph demonstrated a large right-sided lung mass. Further investigations included CT, CT-guided biopsy and PET CT which were discussed at multidisciplinary team meetings. The patient then underwent complete surgical excision. We report this rare malignancy with radiological and pathological features, comparing them with previously reported cases.
Keywords: cardiothoracic surgery; lung cancer (oncology); pathology; radiology.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2021. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Classic biphasic pulmonary blastoma: A case report and review of the literature from 2000 to 2022.Clin Respir J. 2023 Nov;17(11):1103-1116. doi: 10.1111/crj.13701. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Clin Respir J. 2023. PMID: 37772674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Case report of pulmonary biphasic tumor with unusual follow-up].Rev Pneumol Clin. 2014 Oct;70(5):302-6. doi: 10.1016/j.pneumo.2014.01.001. Epub 2014 Mar 16. Rev Pneumol Clin. 2014. PMID: 24646787 French.
-
The Radiologic and Pathologic Diagnosis of Biphasic Pulmonary Blastoma.J Radiol Case Rep. 2017 Sep 30;11(9):10-21. doi: 10.3941/jrcr.v11i9.3153. eCollection 2017 Sep. J Radiol Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 29299105 Free PMC article.
-
Survival of biphasic pulmonary blastoma.Respir Med. 2006 Jul;100(7):1174-9. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2005.10.026. Epub 2005 Dec 5. Respir Med. 2006. PMID: 16332433
-
Pulmonary blastoma: a case report and review of the literature.BMC Res Notes. 2014 May 13;7:294. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-7-294. BMC Res Notes. 2014. PMID: 24885892 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epidemiological characteristics and prognostic risk factors of pulmonary blastoma based on the 2021 WHO classification.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):20963. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-08571-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40594926 Free PMC article.
-
Classic biphasic pulmonary blastoma with endobronchial invasion in a 16-year-old male: A rare case report.Respir Med Case Rep. 2024 Nov 19;52:102143. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2024.102143. eCollection 2024. Respir Med Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39654606 Free PMC article.
-
Classic biphasic pulmonary blastoma: A case report and review of the literature from 2000 to 2022.Clin Respir J. 2023 Nov;17(11):1103-1116. doi: 10.1111/crj.13701. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Clin Respir J. 2023. PMID: 37772674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulmonary blastoma treatment response to anti-PD-1 therapy: a rare case report and literature review.Front Oncol. 2023 Apr 12;13:1146204. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1146204. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37124510 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
