Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on rural communities: a cross-sectional study in the Sichuan Province of China
- PMID: 34376445
- PMCID: PMC8359857
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-046745
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on rural communities: a cross-sectional study in the Sichuan Province of China
Abstract
Objective: Recently, China has experienced a considerable influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on the local people's health and economy. Hence, the current research aims to investigate the psychological and socioeconomic impact of COVID-19 on rural communities in the Sichuan Province of China.
Methods: A total of 499 participants (village representatives of Sichuan Province) were approached to partake in a cross-sectional online survey and share their experience regarding the ongoing pandemic. The descriptive statistics and ordinary least squares (OLS) regression were used to analyse the data.
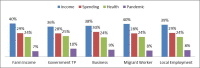
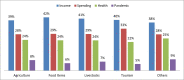
Results: Our analysis revealed that the pandemic has significantly affected local people psychologically, leading to socioeconomic vulnerability. Notably, we find that local households are worried about their income losses regardless of their socioeconomic status (40%-43%), level of income (37%-43%) and industry involvement (38%-43%). However, as income increases, the level of stress decreases. The results further show that government transfer payment is a significant factor in reducing stress due to its reliable and uninterrupted income flow. Contrary to our proposition, the pandemic stress was less observed, which might be because of people's trust in government and effective antiepidemic countermeasures to contain the disease.
Conclusion: This study finds that COVID-19 has a significant impact on local people's health, psychology and income. This study is one of the first to provide empirical evidence regarding the early health and socioeconomic effects of COVID-19 at the household level in rural communities, which are very important to devise policies to ease the outbreak and prevent further losses at the local community level.
Keywords: COVID-19; public health.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- United Nations . Policy brief: COVID-19 and the need for action on mental health. United Nations, 2020.
-
- Shafi M, Liu J, Ren W. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on micro, small, and medium-sized Enterprises operating in Pakistan. Research in Globalization 2020;2:100018. 10.1016/j.resglo.2020.100018 - DOI
-
- UNCTAD . The Covid-19 Shock to Developing Countries: Towards a “whatever it takes” programme for the two-thirds of the world’s population being left behind. United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical