Region-Specific Differences in the Apoe4-dependent Response to Focal Brain Injury
- PMID: 34376629
- PMCID: PMC8424383
- DOI: 10.5607/en21022
Region-Specific Differences in the Apoe4-dependent Response to Focal Brain Injury
Abstract
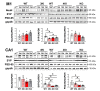
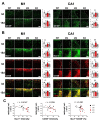
Apolipoprotein E (apoE) plays a role in various physiological functions including lipid transport, synaptic plasticity, and immune modulation. Epidemiological studies suggest that the apoE4 allele increases the risk of post-traumatic sequelae. This study was performed to investigate regionspecific effects of the apoE4 isoform on post-traumatic neurodegeneration. Two focal brain injuries were introduced separately in the motor cortex and hippocampus of apoE4 knock-in, apoE3 knock-in, apoE knockout, and wild-type (WT) mice. Western blotting showed that the expression levels of pre-synaptic and post-synaptic markers at the recovery stage were lower in the hippocampal injury core in apoE4 mice, compared with apoE3 and WT mice. Fast glial activation (determined by immunohistochemistry with glial fibrillary acidic protein, ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1, and cluster of differentiation 45 antibodies) was characteristic of apoE4 mice with hippocampal injury penumbra. apoE4-specific changes were not observed after cortical injury. The intensity of microglial activation in the hippocampus was inversely correlated with the volume of injury reduction on sequential magnetic resonance imaging examinations, when validated using matched samples. These findings indicate that the effects of the interaction between apoE4 and focal brain damage are specific to the hippocampus. Manipulation of inflammatory cell responses could be beneficial for reducing post-traumatic hippocampal neurodegeneration in apoE4 carriers.
Keywords: Apolipoprotein E4; Brain injuries; Hippocampus; Inflammation; Neurodegeneration; Neuroglia.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

