The continuity of effect of schizophrenia polygenic risk score and patterns of cannabis use on transdiagnostic symptom dimensions at first-episode psychosis: findings from the EU-GEI study
- PMID: 34376640
- PMCID: PMC8355107
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-021-01526-0
The continuity of effect of schizophrenia polygenic risk score and patterns of cannabis use on transdiagnostic symptom dimensions at first-episode psychosis: findings from the EU-GEI study
Abstract
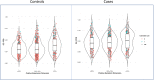
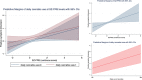
Diagnostic categories do not completely reflect the heterogeneous expression of psychosis. Using data from the EU-GEI study, we evaluated the impact of schizophrenia polygenic risk score (SZ-PRS) and patterns of cannabis use on the transdiagnostic expression of psychosis. We analysed first-episode psychosis patients (FEP) and controls, generating transdiagnostic dimensions of psychotic symptoms and experiences using item response bi-factor modelling. Linear regression was used to test the associations between these dimensions and SZ-PRS, as well as the combined effect of SZ-PRS and cannabis use on the dimensions of positive psychotic symptoms and experiences. We found associations between SZ-PRS and (1) both negative (B = 0.18; 95%CI 0.03-0.33) and positive (B = 0.19; 95%CI 0.03-0.35) symptom dimensions in 617 FEP patients, regardless of their categorical diagnosis; and (2) all the psychotic experience dimensions in 979 controls. We did not observe associations between SZ-PRS and the general and affective dimensions in FEP. Daily and current cannabis use were associated with the positive dimensions in FEP (B = 0.31; 95%CI 0.11-0.52) and in controls (B = 0.26; 95%CI 0.06-0.46), over and above SZ-PRS. We provide evidence that genetic liability to schizophrenia and cannabis use map onto transdiagnostic symptom dimensions, supporting the validity and utility of the dimensional representation of psychosis. In our sample, genetic liability to schizophrenia correlated with more severe psychosis presentation, and cannabis use conferred risk to positive symptomatology beyond the genetic risk. Our findings support the hypothesis that psychotic experiences in the general population have similar genetic substrates as clinical disorders.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M Di Forti reports personal fees from Janssen, outside the submitted work. RM Murray reports personal fees from Janssen, Lundbeck, Sunovion, and Otsuka, outside of the submitted work. M Bernardo reports grants and personal fees from Adamed, Janssen-Cilag, Otsuka, and Abbiotics; personal fees from Angelini and Casen Recordati; and grants from Lundbeck and Takeda, outside of the submitted work. PB Jones reports personal fees from being a member of the scientific advisory boards for Janssen and Recordati, outside of the submitted work. C Arango reports personal fees from Acadia, Ambrosseti, Gedeon Richter, Janssen Cilag, Lundbeck, Merck, Otsuka, Roche, Servier, Shire, Schering Plough, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Sunovion, and Takeda; and grants from CIBERSAM, Familia Alonso, Fundacion Alicia Koplowitz, the European Commission, the Spanish Ministry of Science and Universities, and the Comunidad de Madrid, during the conduct of the study. J Bobes has received research grants and served as consultant, advisor or speaker for AB-Biotics, Acadia Pharmaceuticals, Ambrosseti-Angelini, Casen Recordati, D&A Pharma, Exeltis, Gilead, Indivior, Janssen-Cilag, Lundbeck, Mundipharma, Otsuka, Pfizer, Roche, Sage Therapeutics, Servier, Schwabe Farma Ibérica, Shire, Takeda, research funding from the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competiveness –Centro de Investigación Biomedica en Red area de Salud Mental (CIBERSAM) and Instituto de Salud Carlos III-, Spanish Ministry of Health, Social Services and Equality - Plan Nacional sobre Drogas outside of the submitted work. Dr. Diego Quattrone reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Ulrich Reininghaus reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Alexander L Richards reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Giada Tripoli reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Laura Ferraro reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Paolo Marino reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Andrea Quattrone reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Victoria Rodriguez reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Edoardo Spinazzola reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Charlotte Gayer-Anderson reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Hannah E Jongsma reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Caterina La Cascia reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Prof. Daniele La Barbera reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Ilaria Tarricone reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Elena Bonora reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Sarah Tosato reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Antonio Lasalvia reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Andrei Szöke reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Cristina Marta Del-Ben reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Paulo Rossi Menezes reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Pierre-Michel Llorca reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Jose Luis Santos reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Julio Sanjuán reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Andrea Tortelli reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Eva Velthorst reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Steven Berendsen reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Lieuwe de Haan reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Bart PF Rutten reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Michael Lynskey reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Tom P Freeman reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. James B Kirkbride reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Pak C Sham reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Alastair G Cardno reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Evangelos Vassos reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Michael O’ Donovan is supported by a collaborative research grant from Takeda outside of the submitted work. Dr. Jim van Os reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Craig Morgan reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Cathryn M Lewis reported no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Linscott RJ, van Os J. Systematic reviews of categorical versus continuum models in psychosis: evidence for discontinuous subpopulations underlying a psychometric continuum. Implications for DSM-V, DSM-VI, and DSM-VII. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2010;6:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.032408.153506. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

