SERPINH1, Targeted by miR-29b, Modulated Proliferation and Migration of Human Retinal Endothelial Cells Under High Glucose Conditions
- PMID: 34377003
- PMCID: PMC8350151
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S307771
SERPINH1, Targeted by miR-29b, Modulated Proliferation and Migration of Human Retinal Endothelial Cells Under High Glucose Conditions
Abstract
Aim: In the present study, we performed bioinformatics studies and in vitro functional assays to explore the underlying role of serpin family H member 1 (SERPINH1) in the diabetic retinopathy.
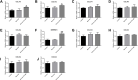
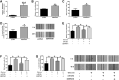
Methods: Common differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between diabetic retinal tissues and normal retinal tissues were analyzed using Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. The proliferation and migration of human retinal endothelial cells (HRECs) was evaluated by MTS, EdU and wound healing assays, respectively; the miRNA and mRNAs expression levels of hub genes in HRECs were determined using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Protein levels were determined using a Western blot assay.
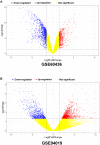
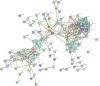
Results: A total of 189 common DEGs were screened between two GEO datasets (GSE60436 and GSE94019), and ten potential hub genes that may link to the progression of diabetic retinopathy were detected. The qRT-PCR results showed that collagen, type I, alpha 1 (COL1A1), Collagen, type I, alpha 2 (COL1A2) and serpin family H member 1 (SERPINH1) mRNA expression levels were up-regulated in the HRECs after being exposed to high glucose for 48 h. Silence of SERPINH1 repressed the high glucose-induced increase in proliferation and migration of HRECs. SERPINH1 was a target of miR-29b and was suppressed by miR-29 in HRECs. SERPINH1 overexpression promoted HREC proliferation and migration. Furthermore, miR-29b suppressed HREC proliferation and migration under high-glucose stimulation, which was significantly attenuated by enforced expression of SERPINH1.
Conclusion: In conclusion, by performing the integrated bioinformatics analysis, the present study suggested that 3 hub genes (COL1A1, COL1A2 and SERPINH1) may be associated with diabetic retinopathy pathophysiology. Further mechanistic studies indicated that miR-29b/SERPINH1 signaling participated in high glucose-induced enhancement in the proliferation and migration of HRECs.
Keywords: HRECs; SERPINH1; bioinformatics analysis; diabetic retinopathy; migration; proliferation.
© 2021 Hu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

