Parkinson's Disease Associated with GBA Gene Mutations: Molecular Aspects and Potential Treatment Approaches
- PMID: 34377557
- PMCID: PMC8327146
- DOI: 10.32607/actanaturae.11031
Parkinson's Disease Associated with GBA Gene Mutations: Molecular Aspects and Potential Treatment Approaches
Abstract
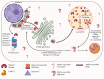
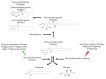
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a multifactorial neurodegenerative disease. To date, genome-wide association studies have identified more than 70 loci associated with the risk of PD. Variants in the GBA gene encoding glucocerebrosidase are quite often found in PD patients in all populations across the world, which justifies intensive investigation of this gene. A number of biochemical features have been identified in patients with GBA-associated Parkinson's disease (GBA-PD). In particular, these include decreased activity of glucocerebrosidase and accumulation of the glucosylceramide substrate. These features were the basis for putting forward a hypothesis about treatment of GBA-PD using new strategies aimed at restoring glucocerebrosidase activity and reducing the substrate concentration. This paper discusses the molecular and genetic mechanisms of GBA-PD pathogenesis and potential approaches to the treatment of this form of the disease.
Keywords: GBA; Parkinson’s disease; glucocerebrosidase; treatment.
Copyright ® 2021 National Research University Higher School of Economics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glucocerebrosidase Mutations Cause Mitochondrial and Lysosomal Dysfunction in Parkinson's Disease: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Implications.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Mar 23;14:851135. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.851135. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35401150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in GBA-associated Parkinson's disease--Pathology, presentation and therapies.Neurochem Int. 2016 Feb;93:6-25. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2015.12.004. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Neurochem Int. 2016. PMID: 26743617 Review.
-
Glucocerebrosidase activity in Parkinson's disease with and without GBA mutations.Brain. 2015 Sep;138(Pt 9):2648-58. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv179. Epub 2015 Jun 27. Brain. 2015. PMID: 26117366 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talks among GBA mutations, glucocerebrosidase, and α-synuclein in GBA-associated Parkinson's disease and their targeted therapeutic approaches: a comprehensive review.Transl Neurodegener. 2021 Jan 15;10(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s40035-020-00226-x. Transl Neurodegener. 2021. PMID: 33446243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GBA mutations, glucosylceramide and Parkinson's disease.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2022 Feb;72:148-154. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2021.11.004. Epub 2021 Dec 6. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 34883387 Review.
Cited by
-
IPSC-Derived Astrocytes Contribute to In Vitro Modeling of Parkinson's Disease Caused by the GBA1 N370S Mutation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 26;25(1):327. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010327. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203497 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroinflammation in Parkinson's Disease: From Gene to Clinic: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 17;24(6):5792. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065792. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982866 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing precision medicine therapeutics for Parkinson's utilizing a shared quantitative systems pharmacology model and framework.Front Syst Biol. 2024 Mar 8;4:1351555. doi: 10.3389/fsysb.2024.1351555. eCollection 2024. Front Syst Biol. 2024. PMID: 40809117 Free PMC article.
-
A dual-functional substrate for quantitation of substrate levels and GCase activity in living cells.RSC Chem Biol. 2025 Jul 3;6(8):1297-1305. doi: 10.1039/d5cb00045a. eCollection 2025 Jul 30. RSC Chem Biol. 2025. PMID: 40621605 Free PMC article.
-
Current Treatments and New, Tentative Therapies for Parkinson's Disease.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 25;15(3):770. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030770. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36986631 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McCann H., Stevens C.H., Cartwright H., Halliday G.M.. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014;20(1):S62–S67. - PubMed
-
- Ascherio A., Schwarzschild M.A.. Lancet Neurol. 2016;15:1257–1272. - PubMed
-
- Agid Y.. Lancet. 1991;337:1321–1324. - PubMed
-
- Schulz J.B., Falkenburger B.H.. Cell Tissue Res. 2004;318:135–147. - PubMed
-
- Hirsch E., Graybiel A.M., Agid Y.A.. Nature. 1988;334:345–348. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources