Determination of benchmark doses for linear furanocoumarin consumption associated with inhibition of cytochrome P450 1A2 isoenzyme activity in healthy human adults
- PMID: 34377680
- PMCID: PMC8329502
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.07.013
Determination of benchmark doses for linear furanocoumarin consumption associated with inhibition of cytochrome P450 1A2 isoenzyme activity in healthy human adults
Abstract
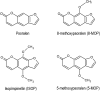
Millions of individuals globally consume traditional herbal medicines (THMs), which contain abundant amounts of linear furanocoumarins. Linear furanocoumarins (i.e., 8-methoxypsoralen, 5-methoxypsoralen, and isopimpinellin) are inhibitors of cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoenzymes including 1A2, a major enzyme involved in drug metabolism and carcinogen bioactivation. Despite the high consumption of furanocoumarin-containing THMs, no studies have measured the furanocoumarin consumption level that triggers an inhibition to CYP1A2 activity in humans. The first objective was to verify if the potencies of the three furanocoumarins are additive towards the inhibition of CYP1A2 activity in vitro using concentration-addition and whole-mixture chemical-mixture-assessment models. A second objective was to determine the benchmark dose (BMD) with the mixtures of furanocoumarin oral doses, expressed as 8-MOP equivalents, and to assess the in vivo CYP1A2 activity, expressed as inhibition percentages. The in vitro results indicated that the three furanocoumarin inhibitory potencies were additive in the THM extracts, validating the use of the concentration-addition model in total furanocoumarin dose-equivalent calculations. Using the USEPA BMD software, the BMD was 18.9 μg 8-MOP equivalent/kg body weight. This information is crucial for furanocoumarin-related health-assessment studies and the regulation of THMs. Further studies should be performed for the remaining major metabolic enzymes to complete the safety profile of furanocoumarin-containing THMs and to provide accurate warning labelling.
Keywords: 5-MOP, 5-methoxypsoralen; 8-MOP, 8-methoxypsoralen; AIC, Akaike’s information criterion; BMD, benchmark dose; BMDL, BMD lower bound; BMDS, BMD software; BMDU, BMD upper bound; BMR, benchmark response; Benchmark dose; CA, concentration-addition model; CYP, cytochrome P450; Caffeine; Cytochrome 1A2 enzyme; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; Furanocoumarin; HLM, human liver microsomes; HPLC, high-performance liquid chromatography; IC50, concentration at 50 % inhibition; ISOP, isopimpinellin; LOAEL, lowest-observed-adverse-effect level; Metabolism; NADPH, β-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen; NOAEL, no-observed-adverse-effect level; POD, point-of-departure; RPF, relative potency factor; SD, standard deviation; TCL, treated clearance; THM, traditional herbal medicine; Traditional herbal medicines; UCL, untreated clearance; USEPA, United States Environmental Protection Agency; WM, whole-mixture model; log10, common log.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Hu M., Fan L., Zhou H.H., Tomlinson B. Theranostics meets traditional Chinese medicine: rational prediction of drug–herb interactions. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2012;12(8):815–830. - PubMed
-
- Pathak M.A., Daniels F., Jr., Fitzpatrick T.B. The presently known distribution of furocoumarins (psoralens) in plants. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1962;39(3):225–239. - PubMed
-
- Bailey D.G., Spence J.D., Munoz C., Arnold J.M.O. Interaction of citrus juices with felodipine and nifedipine. Lancet. 1991;337(8736):268–269. - PubMed
-
- Mays D.C., Camisa C., Cheney P., Pacula C.M., Nawoot S., Gerber N. Methoxsalen is a potent inhibitor of the metabolism of caffeine in humans. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1987;42(6):621–626. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

