Visualization of wrist anatomy-a comparison between 7T and 3T MRI
- PMID: 34378077
- PMCID: PMC8795032
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-021-08165-5
Visualization of wrist anatomy-a comparison between 7T and 3T MRI
Abstract
Objective: Injuries to the wrist are, due to its small size and complex anatomical structures, difficult to assess by MR, and surgical interventions such as diagnostic arthroscopy are often necessary. Therefore, improved visualization using non-invasive methods could be of clinical value. As a first step of improvement, the purpose of this study was to evaluate visualization of anatomical structures at 7T compared with 3T MR.
Methods: Eighteen healthy volunteers (three males and three females from each age decade between 20 and 49 years) were examined with 7T and 3T MR. Four musculoskeletal radiologists graded 2D and 3D images on a five-level grading scale for visibility of ligaments, cartilage, nerves, trabecular bone, and tendons, as well as overall image quality (i.e., edge sharpness, perceived tissue contrast, and presence of artefacts). Statistical analysis was done using a visual grading characteristics (VGC) analysis.
Results: Visibility of cartilage, trabecular bone, tendons, nerves, and ligaments was graded significantly higher at 7T with an area under the curve (AUCVGC) of 0.62-0.88 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.50-0.97, p = < 0.0001-0.03) using either 2D or 3D imaging. Imaging with 3T was not graded as superior to 7T for any structure. Image quality was also significantly superior at 7T, except for artefacts, where no significant differences were found.
Conclusions: Tendons, trabecular bone, nerves, and ligaments were all significantly better visualized at 7T compared to 3T.
Key points: • MRI of the wrist at 7T with a commercially available wrist coil is feasible at similar acquisition times as for 3T MRI. • The current study showed 7T to be superior to 3T in the visualization of anatomical structures of the wrist, including ligaments, tendons, nerves, and trabecular bone. • Image quality was significantly superior at 7T, except for artefacts, where no significant differences were found.
Keywords: Area under curve; Carpal joints; Cartilage, articular; Ligaments; Triangular fibrocartilage.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures


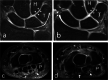
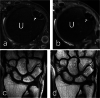
Similar articles
-
Visualization of wrist ligaments with 3D and 2D magnetic resonance imaging at 3 Tesla.Acta Radiol. 2022 Mar;63(3):368-375. doi: 10.1177/0284185121994044. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Acta Radiol. 2022. PMID: 33657847
-
Qualitative and quantitative assessment of wrist MRI at 3.0T: comparison between isotropic 3D turbo spin echo and isotropic 3D fast field echo and 2D turbo spin echo.Acta Radiol. 2013 Apr 1;54(3):284-91. doi: 10.1258/ar.2012.120475. Epub 2013 Jan 14. Acta Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23319720
-
Comparison of Modern 3D and 2D MR Imaging Sequences of the Wrist at 3 Tesla.Rofo. 2016 Aug;188(8):753-62. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-104512. Epub 2016 May 3. Rofo. 2016. PMID: 27139176 English.
-
Anatomy and variants of the triangular fibrocartilage complex and its MR appearance at 3 and 7T.Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2012 Apr;16(2):93-103. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1311761. Epub 2012 May 30. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2012. PMID: 22648425 Review.
-
MR imaging of normal and injured wrist ligaments.Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 1995 May;3(2):229-48. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 1995. PMID: 7553020 Review.
Cited by
-
Sex differences in photon-counting detector computed tomography-derived scaphotrapeziotrapezoid joint morphometrics.Skeletal Radiol. 2025 Sep;54(9):1851-1861. doi: 10.1007/s00256-024-04863-5. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Skeletal Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39907791
-
MRI of wrist ligament trauma was similar at 7 T and 3 T with arthroscopy as a reference standard.Eur Radiol. 2025 May 8. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11656-4. Online ahead of print. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40341973
-
SSR white paper: guidelines for utilization and performance of direct MR arthrography.Skeletal Radiol. 2024 Feb;53(2):209-244. doi: 10.1007/s00256-023-04420-6. Epub 2023 Aug 11. Skeletal Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37566148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ligament reconstruction for distal radioulnar joint instability with the biomechanical analysis: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Oct 11;103(41):e40057. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040057. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39465789 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Bioreactor Design for Non-invasive Longitudinal Monitoring of Tissue-Engineered Heart Valves in 7T MRI and Ultrasound.Ann Biomed Eng. 2025 Feb;53(2):383-397. doi: 10.1007/s10439-024-03632-8. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Ann Biomed Eng. 2025. PMID: 39438348 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nejad N, Carrino JA, Eng J et al (2016) Scapholunate interosseous ligament tears: diagnostic performance of 1.5 T, 3 T MRI, and MR arthrography - a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acad Radiol 23:1091–1103 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

