Anatomical locations of the motor endplates of sartorius muscle for botulinum toxin injections in treatment of muscle spasticity
- PMID: 34378107
- PMCID: PMC8354843
- DOI: 10.1007/s00276-021-02813-7
Anatomical locations of the motor endplates of sartorius muscle for botulinum toxin injections in treatment of muscle spasticity
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to detect the idyllic locations for botulinum neurotoxin injection by analyzing the intramuscular neural distributions of the sartorius muscles.
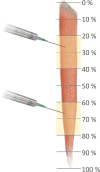
Methods: An altered Sihler's staining was conducted on sartorius muscles (15 specimens). The nerve entry points and intramuscular arborization areas were measured as a percentage of the total distance from the most prominent point of the anterior superior iliac spine (0%) to the medial femoral epicondyle (100%).
Results: Intramuscular neural distribution were densely detected at 20-40% and 60-80% for the sartorius muscles. The result suggests that the treatment of sartorius muscle spasticity requires botulinum neurotoxin injections in particular locations.
Conclusions: These locations, corresponding to the locations of maximum arborization, are suggested as the most suggestive points for botulinum neurotoxin injection.
Keywords: Botulinum neurotoxin; Sartorius muscle; Sihler’s staining; Spasticity.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag France SAS, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
I acknowledge that I have considered the conflict of interest statement included in the “Author Guidelines.” I hereby certify that, to the best of my knowledge, that no aspect of my current personal or professional situation might reasonably be expected to significantly affect my views on the subject I am presenting.
Figures

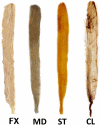

References
-
- Awaad Y, Rizk T, Abak AA, Kabiruddin K, Khoshhal KI. Botulinum toxin-A in postoperative pediatric stiff hips. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2013;8(3):187–191.
-
- Barnes MP, Kent RM, Semlyen JK, McMullen KM. Spasticity in multiple sclerosis. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2003;17(1):66–70. - PubMed
-
- Buckland A, Pan WR, Dhar S, Edwards G, Rozen WM, Ashton MW, Taylor GI. Neurovascular anatomy of sartorius muscle flaps: implications for local transposition and facial reanimation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009;123(1):44–54. - PubMed
-
- Van Campenhout A, Verhaegen A, Pans S, Molenaers G. Botulinum toxin type A injections in the psoas muscle of children with cerebral palsy: muscle atrophy after motor end plate-targeted injections. Res Dev Disabil. 2013;34(3):1052–1058. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

