Profiling the physiological pitfalls of anti-hepatitis C direct-acting agents in budding yeast
- PMID: 34378349
- PMCID: PMC8449668
- DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.13904
Profiling the physiological pitfalls of anti-hepatitis C direct-acting agents in budding yeast
Abstract
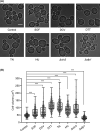
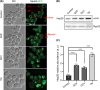
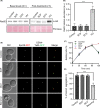
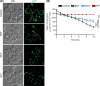
Sofosbuvir and Daclatasvir are among the direct-acting antiviral (DAA) medications prescribed for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C (CHC) virus infection as combination therapy with other antiviral medications. DAA-based therapy achieves high cure rates, reaching up to 97% depending on the genotype of the causative hepatitis C virus (HCV). While DAAs have been approved as an efficient and well-tolerated therapy for CHC, emerging concerns about adverse cardiac side effects, higher risk of recurrence and occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and doubts of genotoxicity have been reported. In our study, we investigated in detail physiological off-targets of DAAs and dissected the effects of these drugs on cellular organelles using budding yeast, a unicellular eukaryotic organism. DAAs were found to disturb the architecture of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the mitochondria, while showing no apparent genotoxicity or DNA damaging effect. Our study provides evidence that DAAs are not associated with genotoxicity and highlights the necessity for adjunctive antioxidant therapy to mitigate the adverse effects of DAAs on ER and mitochondria.
© 2021 The Authors. Microbial Biotechnology published by Society for Applied Microbiology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abouelkheir Abdalla, D., Ali Elhadidy, T., Besheer, T., and Elsayed Farag, R. (2017) Respiratory adverse effects of Sofosbuvir‐based regimens for treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus. Egyptian J Chest Dis Tuberc 66: 363–367.
-
- Allen, J.B., Zhou, Z., Siede, W., Friedberg, E.C., and Elledge, S.J. (1994) The SAD1/RAD53 protein kinase controls multiple checkpoints and DNA damage‐induced transcription in yeast. Genes Dev 8: 2401–2415. - PubMed
-
- Amponsah, P.S., Yahya, G., Zimmermann, J., Mai, M., Mergel, S., Mühlhaus, T., et al. (2021) Peroxiredoxins couple metabolism and cell division in an ultradian cycle. Nat Chem Biol 17: 477–484. - PubMed
-
- Andrade, X.A., Paz, L.H., Nassar, M., Oramas, D.M., Fuentes, H.E., Kovarik, P., et al. (2018) Primary liver diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma following complete response for hepatitis C infection after direct antiviral therapy. Acta Haematol 139: 77–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

