Acute effects of sublingual nitroglycerin on cardiovagal and sympathetic baroreflex sensitivity
- PMID: 34378422
- PMCID: PMC8560367
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00304.2020
Acute effects of sublingual nitroglycerin on cardiovagal and sympathetic baroreflex sensitivity
Abstract
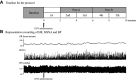
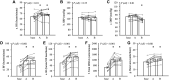
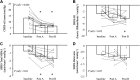
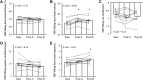
The effects of nitroglycerin (glyceryl trinitrate, GTN) on baroreflex sensitivity (BRS) are incompletely understood. Moreover, there are no reports evaluating the acute responses in both the sympathetic BRS (SBRS) and the cardiovagal BRS (CBRS) to the administration of sublingual GTN. We hypothesized that sublingual GTN modulates both CBRS and SBRS. In 10 healthy subjects, beat-to-beat heart rate (HR), blood pressure (BP), and muscle sympathetic nerve activity (MSNA) were recorded before and for 10 min after sublingual administration of GTN 0.4 mg. SBRS was evaluated from the relationship between spontaneous variations in diastolic BP and MSNA. CBRS was assessed with the sequence technique. These variables were assessed during baseline, during 3rd-6th min (post A), and 7th-10th min (post B) after GTN administration. Two min after GTN administration, MSNA increased significantly and remained significantly elevated during recording. Compared with baseline, CBRS decreased significantly (post A: 12.9 ± 1.6 to 7.1 ± 1.0 ms/mmHg, P < 0.05), whereas SBRS increased significantly (post A: 0.8 ± 0.2 to 1.5 ± 0.2 units·beat-1·mmHg-1, P < 0.05) with an upward shift of the operating point. There were no differences in these variables between posts A and B. A clinical dose of GTN increased MSNA rapidly through effects on both CBRS and SBRS. These effects should be kept in mind when nitrates are used to clinically treat chest pain and acute coronary syndromes and used as vasodilators in experimental settings.
Keywords: baroreflex sensitivity; muscle sympathetic nerve activity; nitrate.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Baroreflex responses to limb venous distension in humans.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2022 Aug 1;323(2):R267-R276. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00028.2022. Epub 2022 Jun 21. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35726869 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of limb suction during arterial occlusion on arterial baroreflex in humans.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2025 Aug 1;329(2):H450-H456. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00365.2025. Epub 2025 Jul 14. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40657785 Free PMC article.
-
Aldosterone impairs baroreflex sensitivity in healthy adults.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Jan;292(1):H190-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00622.2006. Epub 2006 Aug 18. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 16920805
-
Hemodynamic and autonomic effects of low-dose glyceryl trinitrate used to test endothelium-independent vasodilation of the brachial artery.Vascul Pharmacol. 2019 Sep;120:106576. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2019.106576. Epub 2019 Jul 3. Vascul Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31279096
-
Baroreflex sensitivity analysis: spontaneous methodology vs. Valsalva's maneuver.Clin Auton Res. 2013 Jun;23(3):133-9. doi: 10.1007/s10286-013-0195-9. Epub 2013 May 16. Clin Auton Res. 2013. PMID: 23677496
Cited by
-
Acute beetroot juice consumption does not alter cerebral autoregulation or cardiovagal baroreflex sensitivity during lower-body negative pressure in healthy adults.Front Hum Neurosci. 2023 Jan 19;17:1115355. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2023.1115355. eCollection 2023. Front Hum Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36742355 Free PMC article.
-
The role of peripheral venous distension reflex in regulating hemodynamics: mini review.Auton Neurosci. 2024 Dec;256:103217. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2024.103217. Epub 2024 Sep 7. Auton Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39270515 Review.
-
Glucose metabolism and autonomic function in healthy individuals and patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus at rest and during exercise.Exp Physiol. 2024 Feb;109(2):214-226. doi: 10.1113/EP091444. Epub 2023 Dec 5. Exp Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38050866 Free PMC article.
-
Baroreflex responses to limb venous distension in humans.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2022 Aug 1;323(2):R267-R276. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00028.2022. Epub 2022 Jun 21. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35726869 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of limb suction during arterial occlusion on arterial baroreflex in humans.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2025 Aug 1;329(2):H450-H456. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00365.2025. Epub 2025 Jul 14. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40657785 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bath PM, Scutt P, Anderson CS, Appleton JP, Berge E, Cala L, et al. . Prehospital transdermal glyceryl trinitrate in patients with ultra-acute presumed stroke (RIGHT-2): an ambulance-based, randomised, sham-controlled, blinded, phase 3 trial. Lancet 393: 1009–1020, 2019. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30194-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

