Diagnostic merits of the Eosinophilic Esophagitis Diagnostic Panel from a single esophageal biopsy
- PMID: 34380050
- PMCID: PMC8821114
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2021.07.032
Diagnostic merits of the Eosinophilic Esophagitis Diagnostic Panel from a single esophageal biopsy
Abstract
Background: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a histologically "patchy" disease with uneven eosinophil distribution along the esophagus, posing a dilemma for histologically analyzing endoscopic biopsy samples, especially when biopsy samples are limited to only the distal esophagus.
Objective: We investigated whether molecular mRNA profiling of a distal esophageal biopsy sample predicts eosinophilia in the proximal esophagus.
Methods: Esophageal biopsy samples (n = 507) from subjects with EoE were collected from multiple institutions, spanning adults and pediatric patients. Subjects were grouped on the basis of distinct distal (D) and proximal (P) eosinophil counts (D+P+, D+P-, D-P+, and D-P-, with + and - defined as ≥15 or <15 eosinophils/hpf, respectively). Molecular profiles were assessed by using the EoE Diagnostic Panel (EDP), a set of 96 esophageal transcripts used to derive the EDP score.
Results: The distal EDP score was correlated with proximal eosinophil levels (r = -0.73; P < .0001). EDP analysis of a histologically negative distal biopsy sample predicted the presence of proximal esophagitis with high sensitivity (85%). In a 2-year follow-up focusing on the cases with discordant histologic and EDP results, histologically negative patients (D-P-) had higher rates of EoE relapse when the EDP was positive than when the EDP was negative (odds ratio = 11; P = .003), indicating predictive medicine capacity.
Conclusion: EDP analysis of a single distal esophageal biopsy sample predicts remote inflammation in patients with spatially heterogeneous eosinophilia and disease relapse in patients with histologic remission, providing diagnostic merit and predictive medicine capacity for molecular diagnosis of EoE.
Keywords: EoE transcriptome; Eosinophilic esophagitis; diagnostic panel; eosinophil; eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases; molecular diagnostics; predictive medicine.
Copyright © 2021 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
M.E.R. is a consultant for Pulm One, Spoon Guru, Allakos, ClostraBio, Serpin Pharm, Celgene, Shire, Astra Zeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Allakos, Adare, Regeneron, and Novartis and has an equity interest in the first five, as well as royalties from reslizumab (Teva Pharmaceuticals) and Up-To-Date. M.E.R. is an inventor of patents owned by Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. T. S. is a co-inventor of patents owned by Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. T. W. is a co-inventor of patents owned by Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. S.M. has no relevant conflicts of interest.
Figures
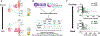
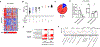
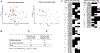
Similar articles
-
Molecular diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis by gene expression profiling.Gastroenterology. 2013 Dec;145(6):1289-99. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.08.046. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23978633 Free PMC article.
-
Yield of esophageal biopsy patterns for the diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis.Gastrointest Endosc. 2025 Aug;102(2):194-201.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2025.01.018. Epub 2025 Jan 18. Gastrointest Endosc. 2025. PMID: 39832555
-
Novel transcriptomic panel identifies histologically active eosinophilic oesophagitis.Gut. 2024 Jun 6;73(7):1076-1086. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-331743. Gut. 2024. PMID: 38670631 Free PMC article.
-
Addressing diagnostic dilemmas in eosinophilic esophagitis using esophageal epithelial eosinophil-derived neurotoxin.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2024 Feb;78(2):304-312. doi: 10.1002/jpn3.12054. Epub 2023 Dec 27. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38374551 Review.
-
Eosinophilic esophagitis.Allergy Asthma Proc. 2019 Nov 1;40(6):462-464. doi: 10.2500/aap.2019.40.4272. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2019. PMID: 31690395 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular analysis of duodenal eosinophilia.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023 Apr;151(4):1027-1039. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2022.12.814. Epub 2022 Dec 30. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36592704 Free PMC article.
-
Host-Microbiota Interactions in the Esophagus During Homeostasis and Allergic Inflammation.Gastroenterology. 2022 Feb;162(2):521-534.e8. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.10.002. Epub 2021 Oct 8. Gastroenterology. 2022. PMID: 34627858 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of sustained remission and reversal of pathologic transcriptome achieved with tezepelumab in an adolescent with eosinophilic esophagitis.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2024 Nov;12(11):3147-3149.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2024.08.013. Epub 2024 Aug 10. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2024. PMID: 39134146 No abstract available.
-
Esophageal Epithelium and Lamina Propria Are Unevenly Involved in Eosinophilic Esophagitis.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Oct;21(11):2807-2816.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.03.014. Epub 2023 Mar 24. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36967100 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and Molecular Contributors in Eosinophilic Esophagitis.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2023 May;23(5):255-266. doi: 10.1007/s11882-023-01075-0. Epub 2023 Apr 21. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2023. PMID: 37084008 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

