Microphysiological Systems: Stakeholder Challenges to Adoption in Drug Development
- PMID: 34380142
- PMCID: PMC8831652
- DOI: 10.1159/000517422
Microphysiological Systems: Stakeholder Challenges to Adoption in Drug Development
Abstract
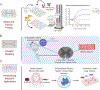
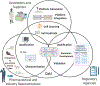
Microphysiological systems (MPS) or tissue chips/organs-on-chips are novel in vitro models that emulate human physiology at the most basic functional level. In this review, we discuss various hurdles to widespread adoption of MPS technology focusing on issues from multiple stakeholder sectors, e.g., academic MPS developers, commercial suppliers of platforms, the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, and regulatory organizations. Broad adoption of MPS technology has thus far been limited by a gap in translation between platform developers, end-users, regulatory agencies, and the pharmaceutical industry. In this brief review, we offer a perspective on the existing barriers and how end-users may help surmount these obstacles to achieve broader adoption of MPS technology.
Keywords: Bioengineering; Drug development; Induced pluripotent stem cells; Microfluidics; Microphysiological systems.
© 2021 This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply. Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
Statements
Conflict of Interest Statement
“The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.”
Figures
References
-
- (2016). BEST (Biomarkers, EndpointS, and other Tools) Resource Silver Spring (MD). - PubMed
-
- Ainslie GR, Davis M, Ewart L, Lieberman LA, Rowlands DJ, Thorley AJ, Yoder G and Ryan AM (2019). “Microphysiological lung models to evaluate the safety of new pharmaceutical modalities: a biopharmaceutical perspective.” Lab Chip 19(19): 3152–3161. - PubMed
-
- Alex A, Harris J and Smith DA (2016). “Attrition in the Pharmaceutical Industry Reasons, Implications, and Pathways Forward Introduction.” Attrition in the Pharmaceutical Industry: Reasons, Implications, and Pathways Forward: 1–4.
-
- Apati A, Varga N, Berecz T, Erdei Z, Homolya L and Sarkadi B (2019). “Application of human pluripotent stem cells and pluripotent stem cell-derived cellular models for assessing drug toxicity.” Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 15(1): 61–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

