Cell therapy strategies for COVID-19: Current approaches and potential applications
- PMID: 34380619
- PMCID: PMC8357240
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abg5995
Cell therapy strategies for COVID-19: Current approaches and potential applications
Abstract
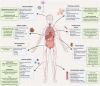
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) continues to burden society worldwide. Despite most patients having a mild course, severe presentations have limited treatment options. COVID-19 manifestations extend beyond the lungs and may affect the cardiovascular, nervous, and other organ systems. Current treatments are nonspecific and do not address potential long-term consequences such as pulmonary fibrosis, demyelination, and ischemic organ damage. Cell therapies offer great potential in treating severe COVID-19 presentations due to their customizability and regenerative function. This review summarizes COVID-19 pathogenesis, respective areas where cell therapies have potential, and the ongoing 89 cell therapy trials in COVID-19 as of 1 January 2021.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 (CC BY).
Figures
References
-
- Wu Z., McGoogan J. M., Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: Summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 323, 1239–1242 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Yang X., Yu Y., Xu J., Shu H., Xia J., Liu H., Wu Y., Zhang L., Yu Z., Fang M., Yu T., Wang Y., Pan S., Zou X., Yuan S., Shang Y., Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir. Med. 8, 475–481 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann M., Kleine-Weber H., Schroeder S., Kruger N., Herrler T., Erichsen S., Schiergens T. S., Herrler G., Wu N. H., Nitsche A., Muller M. A., Drosten C., Pohlmann S., SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell 181, 271–280.e8 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou P., Yang X. L., Wang X. G., Hu B., Zhang L., Zhang W., Si H. R., Zhu Y., Li B., Huang C. L., Chen H. D., Chen J., Luo Y., Guo H., Jiang R. D., Liu M. Q., Chen Y., Shen X. R., Wang X., Zheng X. S., Zhao K., Chen Q. J., Deng F., Liu L. L., Yan B., Zhan F. X., Wang Y. Y., Xiao G. F., Shi Z. L., A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 579, 270–273 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gordon D. E., Jang G. M., Bouhaddou M., Xu J., Obernier K., White K. M., O’Meara M. J., Rezelj V. V., Guo J. Z., Swaney D. L., Tummino T. A., Huettenhain R., Kaake R. M., Richards A. L., Tutuncuoglu B., Foussard H., Batra J., Haas K., Modak M., Kim M., Haas P., Polacco B. J., Braberg H., Fabius J. M., Eckhardt M., Soucheray M., Bennett M. J., Cakir M., McGregor M. J., Li Q., Meyer B., Roesch F., Vallet T., Kain A. M., Miorin L., Moreno E., Naing Z. Z. C., Zhou Y., Peng S., Shi Y., Zhang Z., Shen W., Kirby I. T., Melnyk J. E., Chorba J. S., Lou K., Dai S. A., Barrio-Hernandez I., Memon D., Hernandez-Armenta C., Lyu J., Mathy C. J. P., Perica T., Pilla K. B., Ganesan S. J., Saltzberg D. J., Rakesh R., Liu X., Rosenthal S. B., Calviello L., Venkataramanan S., Liboy-Lugo J., Lin Y., Huang X. P., Liu Y., Wankowicz S. A., Bohn M., Safari M., Ugur F. S., Koh C., Savar N. S., Tran Q. D., Shengjuler D., Fletcher S. J., O’Neal M. C., Cai Y., Chang J. C. J., Broadhurst D. J., Klippsten S., Sharp P. P., Wenzell N. A., Kuzuoglu D., Wang H. Y., Trenker R., Young J. M., Cavero D. A., Hiatt J., Roth T. L., Rathore U., Subramanian A., Noack J., Hubert M., Stroud R. M., Frankel A. D., Rosenberg O. S., Verba K. A., Agard D. A., Ott M., Emerman M., Jura N., von Zastrow M., Verdin E., Ashworth A., Schwartz O., d’Enfert C., Mukherjee S., Jacobson M., Malik H. S., Fujimori D. G., Ideker T., Craik C. S., Floor S. N., Fraser J. S., Gross J. D., Sali A., Roth B. L., Ruggero D., Taunton J., Kortemme T., Beltrao P., Vignuzzi M., Garcia-Sastre A., Shokat K. M., Shoichet B. K., Krogan N. J., A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature 583, 459–468 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

