Mechanism of molnupiravir-induced SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis
- PMID: 34381216
- PMCID: PMC8437801
- DOI: 10.1038/s41594-021-00651-0
Mechanism of molnupiravir-induced SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis
Abstract
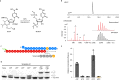
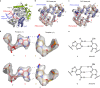
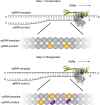
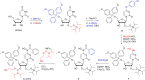
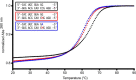
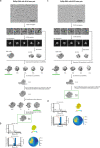
Molnupiravir is an orally available antiviral drug candidate currently in phase III trials for the treatment of patients with COVID-19. Molnupiravir increases the frequency of viral RNA mutations and impairs SARS-CoV-2 replication in animal models and in humans. Here, we establish the molecular mechanisms underlying molnupiravir-induced RNA mutagenesis by the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). Biochemical assays show that the RdRp uses the active form of molnupiravir, β-D-N4-hydroxycytidine (NHC) triphosphate, as a substrate instead of cytidine triphosphate or uridine triphosphate. When the RdRp uses the resulting RNA as a template, NHC directs incorporation of either G or A, leading to mutated RNA products. Structural analysis of RdRp-RNA complexes that contain mutagenesis products shows that NHC can form stable base pairs with either G or A in the RdRp active center, explaining how the polymerase escapes proofreading and synthesizes mutated RNA. This two-step mutagenesis mechanism probably applies to various viral polymerases and can explain the broad-spectrum antiviral activity of molnupiravir.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
A novel model of molnupiravir against SARS-CoV-2 replication: accumulated RNA mutations to induce error catastrophe.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Dec 2;6(1):410. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00837-4. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34857753 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

