Efficacy of AST-120 for Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 34381357
- PMCID: PMC8350440
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.676345
Efficacy of AST-120 for Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
AST-120, an oral spherical activated carbon, may delay the need for kidney dialysis and improve uremia symptoms because it can adsorb acidic and basic organic compounds, especially small-molecule uremic toxins. However, previous studies produced no conclusive evidence regarding the benefits of AST-120 in delaying the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Therefore, this systematic review and network meta-analysis evaluated the effects of AST-120 in patients with CKD. Related keywords of CKD and AST-120 were used to search four databases to obtain potential evidence on this topic, and two authors individually completed evidence selection, data extraction, and quality assessment. Network meta-analysis was performed for mortality, end-stage renal disease, composite renal outcomes, and laboratory outcomes based on a frequentist approach. In total, 15 randomized controlled trials (n = 3,763) were included in the present synthesis, and the pooled results revealed non-significant differences in mortality among the treatment strategies. Low- and high-dose AST-120 were not superior to no AST-120 treatment regarding renal outcomes. However, the event rates of end-stage renal disease (risk ratio [RR] = 0.78, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.62-0.99) and composite renal outcomes (RR = 0.78, 95% CI: 0.63-0.97) were significantly lower in the tailored-dose AST-120 group than in no AST-120 group. The results did not reveal a small-study effect on the outcomes. Tailored dosing of AST-120 appeared to represent an optimal treatment strategy because it resulted in lower rates of composite renal outcomes and end-stage renal disease.
Keywords: adsorbent; chronic renal failure; kremezin; sorbent; uremic toxin.
Copyright © 2021 Su, Lee, Kuo, Chen, Chen, Kang and Chang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
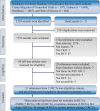


References
-
- Asano Y., Akisawa T., Fukuhara S., Shimojyo F., Matsuo S., Yorioka T., et al. (2008). preventive Effect of the Oral Carbonaceous Absorbent for Progression of Chronic Kidney Failure: Report of a Rct. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai shi 50, 528–531. - PubMed
-
- Baek S. H., Cha R.-h., Kang S. W., Park C. W., Cha D. R., Kim S. G., et al. (2017). Higher Serum Levels of Osteoglycin Are Associated with All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Events in Patients with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 242, 281–290. 10.1620/tjem.242.281 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

