Effectiveness of low-power laser therapy in improvement of the peripheral neuropathy induced by xenobiotics in rats
- PMID: 34381880
- PMCID: PMC8334374
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.101085
Effectiveness of low-power laser therapy in improvement of the peripheral neuropathy induced by xenobiotics in rats
Abstract
Background: Peripheral neuropathy (PN) is the damage and dysfunction of neurons of the peripheral nervous system. The present study was conducted to estimate the effectiveness of low-power laser therapy (LPLT) in the management of PN in a rats' model.
Methods: PN was induced by giving dichloroacetate (DCA) (250 mg/kg/day) for up to 12 weeks. Four groups of rats were used: control group, PN group, PN group treated with gabapentin and PN group treated with LPLT. The study was conducted for 8 weeks. The management of PN was estimated by behavioral tests which included hot plate and Morris water maze tests. Blood biochemical analysis were carried out.
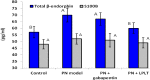
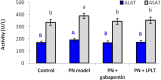
Results: Using of hot plate test indicated thermal hypoalgesia and using Morris water maze test showed cognitive decline in PN rats. Treatment with LPLT or gabapentin improved both the pain sensations and deteriorated memory that occurred in the PN rats. Biochemical analysis showed that LPLT significantly decreased the elevated beta-endorphin level in PN rats, while gabapentin could not reduce it. Treatment PN rats with LPLT or gabapentin shifted the high levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-10 cytokines back to their normal values. Serum nitric oxide and MDA significantly increased in the PN group together with significant reduction in the rGSH level, these values were significantly improved by LPLT application while this was not the case with gabapentin treatment. Furthermore, treatment with gabapentin or LPLT significantly reduced serum ALAT and ASAT activities which are otherwise increased in the PN group. S100B, PGE2, total cholesterol, triglycerides, LDL-cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, urea and creatinine showed insignificant changes among all groups.
Conclusions: Our results showed that treatment with LPLT is more efficient than gabapentin in ameliorating the peripheral neuropathy induced by xenobiotics.
Keywords: ADP, adenosine diphosphate; ATP, Adenosine triphosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; DCA, Dichloroacetate; Dichloroacetate; Gabapentin; IL-10, interleukin −10; IL-1β, interleukin - 1β; LPLT, Low power laser therapy; Low-power laser therapy; MCTs, monocarboxylate transporters; MDA, malondialdehyde; NAD+, Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NO, nitric oxide; Neuropathy; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; PN, Peripheral neuropathy; S100B, calcium binding protein B; TCA, cycle tricarboxylic acid cycle or the Krebs cycle; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor- α; rGSH, reduced glutathione.
© 2021 Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficiencies of Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) and Gabapentin in the Management of Peripheral Neuropathy: Diabetic Neuropathy.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2018 Sep;186(1):161-173. doi: 10.1007/s12010-018-2729-z. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29527628
-
Anti-atherosclerosis of oligomeric proanthocyanidins from Rhodiola rosea on rat model via hypolipemic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory activities together with regulation of endothelial function.Phytomedicine. 2018 Dec 1;51:171-180. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.10.002. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30466614
-
The role of oxidative stress and inflammatory response in high-fat diet induced peripheral neuropathy.J Chem Neuroanat. 2014 Jan;55:51-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2013.12.003. Epub 2014 Jan 7. J Chem Neuroanat. 2014. PMID: 24407112
-
Activation of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Activity by Dichloroacetate Improves Survival and Neurologic Outcomes After Cardiac Arrest in Rats.Shock. 2018 Jun;49(6):704-711. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000971. Shock. 2018. PMID: 28846566
-
Synergistic effect of ellagic acid and gabapentin in a rat model of neuropathic pain.Metab Brain Dis. 2023 Apr;38(4):1421-1432. doi: 10.1007/s11011-023-01190-x. Epub 2023 Feb 22. Metab Brain Dis. 2023. PMID: 36811684
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction/hyperfunction inducing excessive mtROS in inflammatory and neuropathic pain.Mol Pain. 2025 Jan-Dec;21:17448069251359601. doi: 10.1177/17448069251359601. Epub 2025 Jul 5. Mol Pain. 2025. PMID: 40616461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of a physiotherapeutic protocol associated with photobiomodulation for the treatment of leprosy patients.Lasers Med Sci. 2023 Dec 22;39(1):12. doi: 10.1007/s10103-023-03957-1. Lasers Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 38133695
-
IL-10/β-Endorphin-Mediated Neuroimmune Modulation on Microglia during Antinociception.Brain Sci. 2023 May 12;13(5):789. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13050789. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239261 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Daino C. Is there any difference between Diabetic Neuropathy and other forms of Neuropathy? 2017. MCVitamins.com/health%20articles/diabetes-non-diabetic-neuropathy.htm
-
- Chowdhury S.K., Smith D.R., Fernyhough P. The role of aberrant mitochondrial bioenergetics in diabetic neuropathy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013;51:56–65. - PubMed
-
- Li Z., Okamoto K., Hayashi Y., Sheng M. The importance of dendritic mitochondria in the morphogenesis and plasticity of spines and synapses. Cell. 2004;119:873–887. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

