Protocols for endothelial cell isolation from mouse tissues: kidney, spleen, and testis
- PMID: 34382011
- PMCID: PMC8339245
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2021.100523
Protocols for endothelial cell isolation from mouse tissues: kidney, spleen, and testis
Abstract
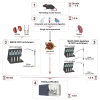
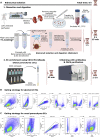
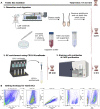
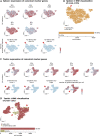
Endothelial cells (ECs) exhibit phenotypic and functional tissue specificities, critical for studies in the vascular field and beyond. Thus, tissue-specific methods for isolation of highly purified ECs are necessary. Kidney, spleen, and testis ECs are relevant players in health and diseases such as chronic kidney disease, acute kidney injury, myelofibrosis, and cancer. Here, we provide tailored protocols for rapid and reproducible EC purification established for scRNA sequencing from these adult murine tissues using the combination of magnetic- and fluorescence-activated cell sorting. For complete details on the use and execution of these protocols, please refer to Kalucka et al. (2020) and Dumas et al. (2020).
Keywords: Cell isolation; Flow Cytometry/Mass Cytometry; Single Cell.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Abraham G., Qiu Y., Inouye M. FlashPCA2: principal component analysis of Biobank-scale genotype datasets. Bioinformatics. 2017;33:2776–2778. - PubMed
-
- Kalucka J., De Rooij L.P.M.H., Goveia J., Rohlenova K., Dumas S.J., Meta E., Conchinha N.V., Taverna F., Teuwen L.-A., Veys K. Single-cell transcriptome atlas of murine endothelial cells. Cell. 2020;180:764–779.e20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

