Temperature-Controlled Radiofrequency Neurolysis for the Treatment of Rhinitis
- PMID: 34382444
- PMCID: PMC8652359
- DOI: 10.1177/19458924211033400
Temperature-Controlled Radiofrequency Neurolysis for the Treatment of Rhinitis
Abstract
Background: Chronic rhinitis is a prevalent condition with a significant impact on quality of life. Posterior nasal nerve and vidian neurectomy are surgical options for treating the symptoms of chronic rhinitis but are invasive procedures.
Objective: To determine the outcomes of patients diagnosed with refractory chronic rhinitis and treated with temperature-controlled radiofrequency neurolysis of the posterior nasal nerve area in a minimally invasive procedure.
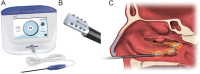
Methods: A prospective, single-arm multicenter study with follow-up through 52 weeks. Eligible adult patients had chronic rhinitis symptoms of at least 6 months duration with inadequate response to at least 4 weeks usage of intranasal steroids and an overall 12-h reflective total nasal symptom score (rTNSS) ≥ 6 with subscores 2 to 3 for rhinorrhea, 1 to 3 for nasal congestion, and 0 to 3 for each of nasal itching and sneezing. Temperature-controlled radiofrequency energy was delivered to the nasal cavity mucosa overlying the posterior nasal nerve region with a novel single-use, disposable, handheld device.
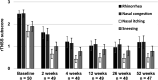
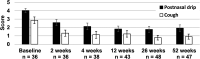
Results: A total of 50 patients were treated (42.0% male; mean age 57.9 ± 11.9 years), and 47 completed the study through 52 weeks. Mean rTNSS significantly improved from 8.5 (95% CI 8.0, 9.0) at baseline to 3.6 (95% CI 3.0, 4.3) at 52 weeks (P < .001), a 57.6% improvement. Similar trends in improvement were noted for rTNSS subscores (rhinorrhea, nasal congestion, itching, sneezing), postnasal drip scores, and chronic cough scores. Subgroup analysis demonstrated the treatment was effective regardless of rhinitis classification (allergic or nonallergic). No serious adverse events with a relationship to the device/procedure occurred.
Conclusions: Temperature-controlled radiofrequency neurolysis of the posterior nasal nerve area for the treatment of chronic rhinitis is safe and resulted in a durable improvement in the symptoms of chronic rhinitis through a 52-week follow-up. Data suggest that this novel device could be considered a minimally invasive option in the otolaryngologist's armamentarium for the treatment of chronic rhinitis.
Keywords: allergic; congestion; neurectomy; neurolysis; posterior nasal nerve; rTNSS; radiofrequency ablation; rhinitis; rhinorrhea; temperature-controlled.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Settipane RA, Charnock DR. Epidemiology of rhinitis: allergic and nonallergic. Clin Allergy Immunol. 2007;19:23–34. - PubMed
-
- Scadding GK, Kariyawasam HH, Scadding G, et al. BSACI Guideline for the diagnosis and management of allergic and non-allergic rhinitis (revised edition 2017; first edition 2007). Clin Exp Allergy. 2017;47(7):856–889. - PubMed
-
- Marshak T, Yun WK, Hazout C, Sacks R, Harvey RJ. A systematic review of the evidence base for vidian neurectomy in managing rhinitis. J Laryngol Otol. 2016;130(Suppl 4):S7–S28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

