Inhibition of MEK pathway enhances the antitumor efficacy of chimeric antigen receptor T cells against neuroblastoma
- PMID: 34382720
- PMCID: PMC8486218
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.15074
Inhibition of MEK pathway enhances the antitumor efficacy of chimeric antigen receptor T cells against neuroblastoma
Abstract
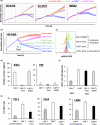
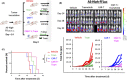
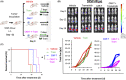
Disialoganglioside (GD2)-specific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells (GD2-CAR-T cells) have been developed and tested in early clinical trials in patients with relapsed/refractory neuroblastoma. However, the effectiveness of immunotherapy using these cells is limited, and requires improvement. Combined therapy with CAR-T cells and molecular targeted drugs could be a promising strategy to enhance the antitumor efficacy of CAR T cell immunotherapy. Here, we generated GD2-CAR-T cells through piggyBac transposon (PB)-based gene transfer (PB-GD2-CAR-T cells), and analyzed the combined effect of these cells and a MEK inhibitor in vitro and in vivo on neuroblastoma. Trametinib, a MEK inhibitor, ameliorated the killing efficacy of PB-GD2-CAR-T cells in vitro, whereas a combined treatment of the two showed superior antitumor efficacy in a murine xenograft model compared to that of PB-GD2-CAR-T cell monotherapy, regardless of the mutation status of the MAPK pathway in tumor cells. The results presented here provide new insights into the feasibility of combined treatment with CAR-T cells and MEK inhibitors in patients with neuroblastoma.
Keywords: CAR-T cell therapy; GD2; MEK inhibitor; chimeric antigen receptor; neuroblastoma; trametinib.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest related to this study.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

