Ambulatory intravenous furosemide for decompensated heart failure: safe, feasible, and effective
- PMID: 34382749
- PMCID: PMC8497198
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.13368
Ambulatory intravenous furosemide for decompensated heart failure: safe, feasible, and effective
Abstract
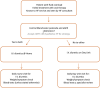
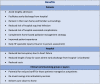
Aims: This study aims to establish the feasibility, safety, and efficacy of outpatient intravenous (IV) diuretic treatment for the management of decompensated heart failure (HF) for patients enrolled in the HeartFailure@Home service.
Methods and results: We retrospectively analysed the clinical episodes of decompensated HF for patients enrolled in the HeartFailure@Home service, managed by ambulatory IV diuretic treatment either at home or on a day-case unit. A control group consisting of HF patients admitted to hospital for IV diuretics (standard-of-care) was also evaluated. In total, 203 episodes of decompensated HF (n = 154 patients) were evaluated. One hundred and fourteen episodes in 79 patients were managed exclusively by the ambulatory IV diuretic service-78 (68.4%) on a day-case unit and 36 (31.6%) domiciliary; 84.1% of patient episodes under the HF@Home service were successfully managed entirely in an out-patient setting without hospitalization. Eleven patients required admission in order to administer higher doses of IV diuretics than could be provided in the ambulatory setting. During follow-up, there were 20 (17.5%) 30 day re-admissions with HF or death in the ambulatory IV group and 29 (32.6%) in the standard-of-care arm (P = 0.02). There was no difference in 30 day HF readmissions between the two groups (14.9% ambulatory vs. 13.5% inpatients, P = 0.8), but 30 day mortality was significantly lower in the ambulatory group (3.5% vs. 21.3% inpatients, P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Outpatient ambulatory management of decompensated HF with IV diuretics given either on a day case unit or in a domiciliary setting is feasible, safe, and effective in selected patients with decompensated HF. This should be explored further as a model in delivering HF services in the outpatient setting during COVID-19.
Keywords: Ambulatory; Diuretics; Elderly; Heart failure; Intravenous.
© 2021 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Cowie MR, Anker SD, Cleland JGF, Felker GM, Filippatos G, Jaarsma T, Jourdain P, Knight E, Massie B, Ponikowski P, López‐Sendón J. Improving care for patients with acute heart failure: before, during and after hospitalization. ESC Heart Fail 2014; 1: 110–145. - PubMed
-
- Braunschweig F, Cowie MR, Auricchio A. What are the costs of heart failure? EP Europace 2011; 13: ii13–ii17. - PubMed
-
- Stewart S, Jenkins A, Buchan S, McGuire A, Capewell S, McMurray JJJV. The current cost of heart failure to the National Health Service in the UK. Eur J Heart Fail 2002; 4: 361–371. - PubMed
-
- Ryder M, Murphy NF, McCaffrey D, O'Loughlin C, Ledwidge M, McDonald K. Outpatient intravenous diuretic therapy; potential for marked reduction in hospitalisations for acute decompensated heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 2008; 10: 267–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

