Accelerated Hypofractionated Image-Guided vs Conventional Radiotherapy for Patients With Stage II/III Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Poor Performance Status: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 34383006
- PMCID: PMC8531992
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.3186
Accelerated Hypofractionated Image-Guided vs Conventional Radiotherapy for Patients With Stage II/III Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Poor Performance Status: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: A significant subset of patients with stage II/III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cannot receive standard concurrent chemoradiotherapy owing to the risk of toxic effects outweighing potential benefits. Without concurrent chemotherapy, however, the efficacy of conventional radiotherapy is reduced.
Objective: To determine whether hypofractionated image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) would improve overall survival in patients with stage II/III NSCLC who could not receive concurrent chemoradiotherapy and therefore were traditionally relegated to receiving only conventionally fractionated radiotherapy (CFRT).
Design, setting, and participants: This nonblinded, phase 3 randomized clinical study enrolled 103 patients and analyzed 96 patients with stage II/III NSCLC and Zubrod performance status of at least 2, with greater than 10% weight loss in the previous 6 months, and/or who were ineligible for concurrent chemoradiotherapy after oncology consultation. Enrollment occurred at multiple US institutions. Patients were enrolled from November 13, 2012, to August 28, 2018, with a median follow-up of 8.7 (3.6-19.9) months. Data were analyzed from September 14, 2018, to April 11, 2021.
Interventions: Eligible patients were randomized to hypofractionated IGRT (60 Gy in 15 fractions) vs CFRT (60 Gy in 30 fractions).
Main outcomes and measures: The primary end point was 1-year overall survival.
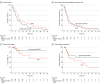
Results: A total of 103 patients (96 of whom were analyzed [63 men (65.6%); mean (SD) age, 71.0 (10.2) years (range, 50-90 years)]) were randomized to hypofractionated IGRT (n = 50) or CFRT (n = 46) when a planned interim analysis suggested futility in reaching the primary end point, and the study was closed to further accrual. There was no statistically significant difference between the treatment groups for 1-year overall survival (37.7% [95% CI, 24.2%-51.0%] for hypofractionated IGRT vs 44.6% [95% CI, 29.9%-58.3%] for CFRT; P = .29). There were also no significant differences in median overall survival, progression-free survival, time to local failure, time to distant metastasis, and toxic effects of grade 3 or greater between the 2 treatment groups.
Conclusions and relevance: This phase 3 randomized clinical trial found that hypofractionated IGRT (60 Gy in 15 fractions) was not superior to CFRT (60 Gy in 30 fractions) for patients with stage II/III NSCLC ineligible for concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Further studies are needed to verify equivalence between these radiotherapy regimens. Regardless, for well-selected patients with NSCLC (ie, peripheral primary tumors and limited mediastinal/hilar adenopathy), the convenience of hypofractionated radiotherapy regimens may offer an appropriate treatment option.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01459497.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Radiation Dose and Fractionation in Locally Advanced Lung Cancer: A Simple Question With a Complicated Answer.JAMA Oncol. 2021 Oct 1;7(10):1505-1506. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.3180. JAMA Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34383023 No abstract available.
-
Hypofractionated Radiotherapy for Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer-Does Size Matter?JAMA Oncol. 2022 Mar 1;8(3):480-481. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.7157. JAMA Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35024782 No abstract available.
-
Hypofractionated Radiotherapy for Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer-Does Size Matter?-Reply.JAMA Oncol. 2022 Mar 1;8(3):481. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.7160. JAMA Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35024789 No abstract available.
References
-
- Komaki R, Scott C, Ettinger D, et al. . Randomized study of chemotherapy/radiation therapy combinations for favorable patients with locally advanced inoperable nonsmall cell lung cancer: Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) 92-04. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1997;38(1):149-155. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(97)00251-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Komaki R, Seiferheld W, Ettinger D, Lee JS, Movsas B, Sause W. Randomized phase II chemotherapy and radiotherapy trial for patients with locally advanced inoperable non–small-cell lung cancer: long-term follow-up of RTOG 92-04. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;53(3):548-557. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(02)02793-1 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

