atg7-Based Autophagy Activation Reverses Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity
- PMID: 34384247
- PMCID: PMC8484060
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.319104
atg7-Based Autophagy Activation Reverses Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity
Abstract
[Figure: see text].
Keywords: anthracycline; autophagy; cardiotoxicity; doxorubicin; zebrafish.
Figures


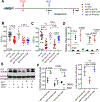


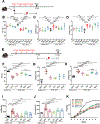
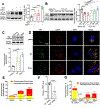

Comment in
-
Activating Autophagy to Prevent Doxorubicin Cardiomyopathy: The Timing Matters.Circ Res. 2021 Oct;129(8):801-803. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.320063. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Circ Res. 2021. PMID: 34591656 No abstract available.
References
-
- Zamorano JL, Lancellotti P, Rodriguez Munoz D, Aboyans V, Asteggiano R, Galderisi M, Habib G, Lenihan DJ, Lip GYH, Lyon AR, Lopez Fernandez T, Mohty D, Piepoli MF, Tamargo J, Torbicki A, Suter TM and Group ESCSD. 2016 ESC Position Paper on cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity developed under the auspices of the ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines: The Task Force for cancer treatments and cardiovascular toxicity of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2016;37:2768–2801. - PubMed
-
- FELKER RET GM, HARE JM, HRUBAN RH, CLEMETSON DE, HOWARD DL, BAUGHMAN KL, AND KASPER EK. Underlying causes and long-term survival in patients with initially unexplaine cardiomyopathy. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2000;342:1077–1084. - PubMed
-
- Vejpongsa P and Yeh ET. Prevention of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity: challenges and opportunities. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64:938–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

