Proteomic landscape of Alzheimer's Disease: novel insights into pathogenesis and biomarker discovery
- PMID: 34384464
- PMCID: PMC8359598
- DOI: 10.1186/s13024-021-00474-z
Proteomic landscape of Alzheimer's Disease: novel insights into pathogenesis and biomarker discovery
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Proteomic landscape of Alzheimer's Disease: novel insights into pathogenesis and biomarker discovery.Mol Neurodegener. 2021 Oct 20;16(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s13024-021-00493-w. Mol Neurodegener. 2021. PMID: 34670601 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
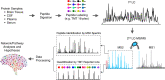
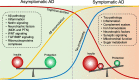
Mass spectrometry-based proteomics empowers deep profiling of proteome and protein posttranslational modifications (PTMs) in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Here we review the advances and limitations in historic and recent AD proteomic research. Complementary to genetic mapping, proteomic studies not only validate canonical amyloid and tau pathways, but also uncover novel components in broad protein networks, such as RNA splicing, development, immunity, membrane transport, lipid metabolism, synaptic function, and mitochondrial activity. Meta-analysis of seven deep datasets reveals 2,698 differentially expressed (DE) proteins in the landscape of AD brain proteome (n = 12,017 proteins/genes), covering 35 reported AD genes and risk loci. The DE proteins contain cellular markers enriched in neurons, microglia, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and epithelial cells, supporting the involvement of diverse cell types in AD pathology. We discuss the hypothesized protective or detrimental roles of selected DE proteins, emphasizing top proteins in "amyloidome" (all biomolecules in amyloid plaques) and disease progression. Comprehensive PTM analysis represents another layer of molecular events in AD. In particular, tau PTMs are correlated with disease stages and indicate the heterogeneity of individual AD patients. Moreover, the unprecedented proteomic coverage of biofluids, such as cerebrospinal fluid and serum, procures novel putative AD biomarkers through meta-analysis. Thus, proteomics-driven systems biology presents a new frontier to link genotype, proteotype, and phenotype, accelerating the development of improved AD models and treatment strategies.
Keywords: Abeta; Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloidome; Biomarker; Mass spectrometry; PTM; Pathogenesis; Proteome; Proteomics; Tau.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.
Figures




References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2020;2020(16):391–460. - PubMed
-
- Alzheimer’s Disease Interenational. World Alzheimer Report 2018 The state of the art of dementia research: New frontiers. 2018.
-
- Scheltens P, et al. Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet. 2016;388:505–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

