Musculoskeletal magnetic resonance imaging in the DE50-MD dog model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 34384671
- PMCID: PMC8449064
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nmd.2021.05.010
Musculoskeletal magnetic resonance imaging in the DE50-MD dog model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Abstract
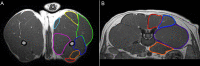
The DE50-MD canine model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) has a dystrophin gene splice site mutation causing deletion of exon 50, an out-of-frame transcript and absence of dystrophin expression in striated muscles. We hypothesized that the musculoskeletal phenotype of DE50-MD dogs could be detected using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), that it would progress with age and that it would reflect those in other canine models and DMD patients. 15 DE50-MD and 10 age-matched littermate wild type (WT) male dogs underwent MRI every 3 months from 3 to 18 months of age. Normalized muscle volumes, global muscle T2 and ratio of post- to pre-gadolinium T1-weighted SI were evaluated in 7 pelvic limb and 4 lumbar muscles bilaterally. DE50-MD dogs, compared to WT, had smaller volumes in all muscles, except the cranial sartorius; global muscle T2 was significantly higher in DE50-MD dogs compared to WT. Muscle volumes plateaued and global muscle T2 decreased with age. Normalized muscle volumes and global muscle T2 revealed significant differences between groups longitudinally and should be useful to determine efficacy of therapeutics in this model with suitable power and low sample sizes. Musculoskeletal changes reflect those of DMD patients and other dog models.
Keywords: DE50-MD; DMD; Imaging biomarkers; MRI; Musculoskeletal.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations of Competing Interest Richard Piercy is a consultant to Exonic Therapeutics; the financial interests have been reviewed and approved by the University in accordance with conflict of interest policies. Studies in his lab have been funded by Pfizer and Exonics Therapeutics. Dominic Wells is or has been a consultant to a wide range of companies with interests in the DMD space including Pfizer, Sarepta, Akashi and Actual Analytics. Studies in his lab have been funded by Proximagen and Shire.
Figures








References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

