Durability of mRNA-1273 vaccine-induced antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 variants
- PMID: 34385356
- PMCID: PMC8691522
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abj4176
Durability of mRNA-1273 vaccine-induced antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 variants
Abstract
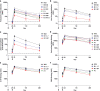
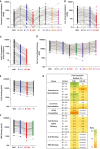
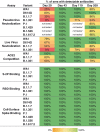
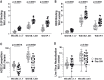
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) mutations may diminish vaccine-induced protective immune responses, particularly as antibody titers wane over time. Here, we assess the effect of SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1.1.7 (Alpha), B.1.351 (Beta), P.1 (Gamma), B.1.429 (Epsilon), B.1.526 (Iota), and B.1.617.2 (Delta) on binding, neutralizing, and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2)–competing antibodies elicited by the messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine mRNA-1273 over 7 months. Cross-reactive neutralizing responses were rare after a single dose. At the peak of response to the second vaccine dose, all individuals had responses to all variants. Binding and functional antibodies against variants persisted in most subjects, albeit at low levels, for 6 months after the primary series of the mRNA-1273 vaccine. Across all assays, B.1.351 had the lowest antibody recognition. These data complement ongoing studies to inform the potential need for additional boost vaccinations.
Figures
Update of
-
Durability of mRNA-1273-induced antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 variants.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 May 16:2021.05.13.444010. doi: 10.1101/2021.05.13.444010. bioRxiv. 2021. Update in: Science. 2021 Sep 17;373(6561):1372-1377. doi: 10.1126/science.abj4176. PMID: 34031659 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU) (2021); https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html.
-
- Edara V. V., Norwood C., Floyd K., Lai L., Davis-Gardner M. E., Hudson W. H., Mantus G., Nyhoff L. E., Adelman M. W., Fineman R., Patel S., Byram R., Gomes D. N., Michael G., Abdullahi H., Beydoun N., Panganiban B., McNair N., Hellmeister K., Pitts J., Winters J., Kleinhenz J., Usher J., O’Keefe J. B., Piantadosi A., Waggoner J. J., Babiker A., Stephens D. S., Anderson E. J., Edupuganti S., Rouphael N., Ahmed R., Wrammert J., Suthar M. S., Infection- and vaccine-induced antibody binding and neutralization of the B.1.351 SARS-CoV-2 variant. Cell Host Microbe 29, 516–521.E3 (2021). 10.1016/j.chom.2021.03.009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann M., Arora P., Groß R., Seidel A., Hörnich B. F., Hahn A. S., Krüger N., Graichen L., Hofmann-Winkler H., Kempf A., Winkler M. S., Schulz S., Jäck H.-M., Jahrsdörfer B., Schrezenmeier H., Müller M., Kleger A., Münch J., Pöhlmann S., SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1.351 and P.1 escape from neutralizing antibodies. Cell 184, 2384–2393.E12 (2021). 10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.036 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang P., Nair M. S., Liu L., Iketani S., Luo Y., Guo Y., Wang M., Yu J., Zhang B., Kwong P. D., Graham B. S., Mascola J. R., Chang J. Y., Yin M. T., Sobieszczyk M., Kyratsous C. A., Shapiro L., Sheng Z., Huang Y., Ho D. D., Antibody resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1.351 and B.1.1.7. Nature 593, 130–135 (2021). 10.1038/s41586-021-03398-2 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

