Daily energy expenditure through the human life course
- PMID: 34385400
- PMCID: PMC8370708
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abe5017
Daily energy expenditure through the human life course
Abstract
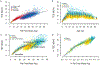
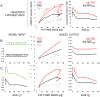
Total daily energy expenditure ("total expenditure") reflects daily energy needs and is a critical variable in human health and physiology, but its trajectory over the life course is poorly studied. We analyzed a large, diverse database of total expenditure measured by the doubly labeled water method for males and females aged 8 days to 95 years. Total expenditure increased with fat-free mass in a power-law manner, with four distinct life stages. Fat-free mass-adjusted expenditure accelerates rapidly in neonates to ~50% above adult values at ~1 year; declines slowly to adult levels by ~20 years; remains stable in adulthood (20 to 60 years), even during pregnancy; then declines in older adults. These changes shed light on human development and aging and should help shape nutrition and health strategies across the life span.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
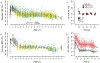
Comment in
-
Taking the long view on metabolism.Science. 2021 Aug 13;373(6556):738-739. doi: 10.1126/science.abl4537. Science. 2021. PMID: 34385381 No abstract available.
References
-
- Henry CJ, Basal metabolic rate studies in humans: measurement and development of new equations. Public Health Nutr 8, 1133–1152 (2005). - PubMed
-
- FAO, Human energy requirements: report of a joint FAO/ WHO/UNU Expert Consultation. Food Nutr Bull 26, 166 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Westerterp KR, de Boer JO, Saris WHM, Schoffelen PFM, ten Hoor F, Measurement of energy expenditure using doubly labelled water. Int J Sport Med 5, S74–75 (1984).
-
- Klein PD et al.Calorimetric validation of the doubly-labelled water method for determination of energy expenditure in man. Hum Nutr Clin Nutr 38, 95–106 (1984). - PubMed
-
- Speakman JR, Doubly Labelled Water: Theory and Practice. (Chapman and Hall, London, 1997).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 AR071160/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK085163/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK080763/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG020480/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG022132/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG029914/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA119171/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA HD000641/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK080760/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG067200/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK030031/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK074387/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK056781/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK068052/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG020478/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR026764/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- Z99 HD999999/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

