Multifaceted Impacts of Periodontal Pathogens in Disorders of the Intestinal Barrier
- PMID: 34386004
- PMCID: PMC8353228
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.693479
Multifaceted Impacts of Periodontal Pathogens in Disorders of the Intestinal Barrier
Abstract
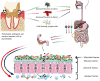
Periodontal disease, a common inflammatory disease, is considered a hazardous factor that contributes to the development of diseases of the digestive system as well as other systems. The bridge between periodontitis and systemic diseases is believed to be periodontal pathogens. The intestine, as part of the lower gastrointestinal tract, has a close connection with the oral cavity. Within the intestine, the intestinal barrier acts as a multifunctional system including microbial, mucous, physical and immune barrier. The intestinal barrier forms the body's first line of defense against external pathogens; its breakdown can lead to pathological changes in the gut and other organs or systems. Reports in the literature have described how oral periodontal pathogens and pathobiont-reactive immune cells can transmigrate to the intestinal mucosa, causing the destruction of intestinal barrier homeostasis. Such findings might lead to novel ideas for investigating the relationship between periodontal disease and other systemic diseases. This review summarizes studies on the effects of periodontal pathogens on the intestinal barrier, which might contribute to understanding the link between periodontitis and gastrointestinal diseases.
Keywords: gut microbiota; immune barrier; intestinal barrier; periodontal pathogens; tight junction.
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Huang, Wang, Ma, Zhang, Lu, Liu and Kou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The multifaceted role of commensal microbiota in homeostasis and gastrointestinal diseases.J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:321241. doi: 10.1155/2015/321241. Epub 2015 Feb 22. J Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 25759839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Roles of Inflammation, Nutrient Availability and the Commensal Microbiota in Enteric Pathogen Infection.Microbiol Spectr. 2015 Jun;3(3). doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MBP-0008-2014. Microbiol Spectr. 2015. PMID: 26185088
-
The Impact of Dietary Sphingolipids on Intestinal Microbiota and Gastrointestinal Immune Homeostasis.Front Immunol. 2021 May 14;12:635704. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.635704. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34054805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The crosstalk between gut bacteria and host immunity in intestinal inflammation.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Apr;236(4):2239-2254. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30024. Epub 2020 Aug 27. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 32853458 Review.
-
Modulation of gut microbiota on intestinal permeability: A novel strategy for treating gastrointestinal related diseases.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Aug 20;137:112416. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112416. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38852521 Review.
Cited by
-
Metformin and risk of gingival/periodontal diseases in diabetes patients: A retrospective cohort study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 5;13:1036885. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1036885. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36277720 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Candida albicans Virulence Factors in the Formation of Multispecies Biofilms With Bacterial Periodontal Pathogens.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jan 5;11:765942. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.765942. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35071033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Periodontal Treatment to Improve General Health and Manage Systemic Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1472:245-260. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-79146-8_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40111696 Review.
-
Valuable effects of lactobacillus and citicoline on steatohepatitis: role of Nrf2/HO-1 and gut microbiota.AMB Express. 2023 Jun 8;13(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13568-023-01561-8. AMB Express. 2023. PMID: 37291355 Free PMC article.
-
Periodontitis salivary microbiota exacerbates colitis-induced anxiety-like behavior via gut microbiota.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2023 Dec 7;9(1):93. doi: 10.1038/s41522-023-00462-9. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2023. PMID: 38062089 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

