The phytochemical, biological, and medicinal attributes of phytoecdysteroids: An updated review
- PMID: 34386319
- PMCID: PMC8343124
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.10.012
The phytochemical, biological, and medicinal attributes of phytoecdysteroids: An updated review
Abstract
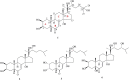
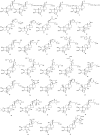
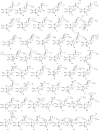
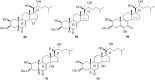
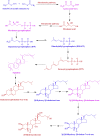
The phytoecdysteroids (PEs) comprise a large group of biologically-active plant steroids, which have structures similar to those of insect-molting hormones. PEs are distributed in plants as secondary metabolites that offer protection against phytophagus (plant-eating) insects. When insects consume the plants containing these chemicals, they promptly molt and undergo metabolic destruction; the insects eventually die. Chemically, ecdysteroids are a group of polyhydroxylated ketosteroids that are structurally similar to androgens. The carbon skeleton of ecdysteroids is termed as cyclopentanoperhydro-phenanthrene with a β-side chain at carbon-17. The essential characteristics of ecdysteroids are a cis-(5β-H) junction of rings A and B, a 7-en-6-one chromophore, and a trans-(14α-OH) junction of rings C and D. Plants only synthesize PEs from mevalonic acid in the mevalonate pathway of the plant cell using acetyl-CoA as a precursor; the most common PE is 20-hydroxyecdysone. So far, over 400 PEs have been identified and reported, and a compilation of 166 PEs originating from 1998 has been previously reviewed. In the present review, we have summarized 212 new PEs reported between 1999 and 2019. We have also critically analyzed the biological, pharmacological, and medicinal properties of PEs to understand the full impact of these phytoconstituents in health and disease.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory; Anticancer activity; Antidiabetic; Antimicrobial; Antioxidant; Phytoecdysteroids; Secondary metabolites.
© 2021 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Phytoecdysteroids: Distribution, Structural Diversity, Biosynthesis, Activity, and Crosstalk with Phytohormones.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 4;23(15):8664. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158664. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosynthesis and distribution of insect-molting hormones in plants--a review.Lipids. 1995 Mar;30(3):257-62. doi: 10.1007/BF02537830. Lipids. 1995. PMID: 7791535 Review.
-
Ecdysteroids in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.): biosynthesis, transport and regulation of levels.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2008 Oct;46(10):844-54. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2008.06.002. Epub 2008 Jun 13. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2008. PMID: 18653353
-
Plant ecdysteroids: plant sterols with intriguing distributions, biological effects and relations to plant hormones.Planta. 2016 Sep;244(3):545-55. doi: 10.1007/s00425-016-2561-z. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Planta. 2016. PMID: 27339274 Review.
-
Biosynthesis of sterols and ecdysteroids in Ajuga hairy roots.Lipids. 2000 Mar;35(3):279-88. doi: 10.1007/s11745-000-0524-z. Lipids. 2000. PMID: 10783005
Cited by
-
The Ethnopharmacological Uses, Metabolite Diversity, and Bioactivity of Rhaponticum uniflorum (Leuzea uniflora): A Comprehensive Review.Biomolecules. 2022 Nov 20;12(11):1720. doi: 10.3390/biom12111720. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36421734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison between the Biological Active Compounds in Plants with Adaptogenic Properties (Rhaponticum carthamoides, Lepidium meyenii, Eleutherococcus senticosus and Panax ginseng).Plants (Basel). 2021 Dec 26;11(1):64. doi: 10.3390/plants11010064. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35009068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytochemical Screening, Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Biomass from Lychnis flos-cuculi L. In Vitro Cultures and Intact Plants.Plants (Basel). 2021 Jan 22;10(2):206. doi: 10.3390/plants10020206. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33499074 Free PMC article.
-
β-ecdysone/PLGA composite scaffolds promote skull defect healing in diabetic rat.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Jan 13;12:1536102. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1536102. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39872465 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory Effect of Helleborus purpurascens Waldst. & Kit.Plants (Basel). 2021 Sep 23;10(10):1990. doi: 10.3390/plants10101990. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34685798 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakanishi K. The ecdysones. Pure Appl Chem. 1971;25:167–195. - PubMed
-
- Butenandt A., Karlson P. About the isolation of a metamorphosis hormone of insects in crystallized form. Z Naturforsch. 1954;9B:389.
-
- Huber R., Hoppe W. On the chemistry of ecdysone. VII. Analysis of the crystal and molecular structure of the molting hormone in insects, ecdysone, using the automized folding molecule method. Chem Ber. 1965;98:2403–2424. - PubMed
-
- Dinan L., Lafont R. Effects and applications of arthropod steroid hormones (ecdysteroids) in mammals. J Endocrinol. 2006;191:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Bathori M., Pongracz Z. Phytoecdysteroids—from isolation to their effects on humans. Curr Med Chem. 2005;12:153–172. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

