Recent advances in nanomedicines for the treatment of ischemic stroke
- PMID: 34386320
- PMCID: PMC8343119
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.11.019
Recent advances in nanomedicines for the treatment of ischemic stroke
Abstract
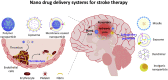
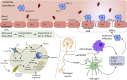
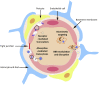
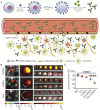
Ischemic stroke is a cerebrovascular disease normally caused by interrupted blood supply to the brain. Ischemia would initiate the cascade reaction consisted of multiple biochemical events in the damaged areas of the brain, where the ischemic cascade eventually leads to cell death and brain infarction. Extensive researches focusing on different stages of the cascade reaction have been conducted with the aim of curing ischemic stroke. However, traditional treatment methods based on antithrombotic therapy and neuroprotective therapy are greatly limited for their poor safety and treatment efficacy. Nanomedicine provides new possibilities for treating stroke as they could improve the pharmacokinetic behavior of drugs in vivo, achieve effective drug accumulation at the target site, enhance the therapeutic effect and meanwhile reduce the side effect. In this review, we comprehensively describe the pathophysiology of stroke, traditional treatment strategies and emerging nanomedicines, summarize the barriers and methods for transporting nanomedicine to the lesions, and illustrate the latest progress of nanomedicine in treating ischemic stroke, with a view to providing a new feasible path for the treatment of cerebral ischemia.
Keywords: AEPO, asialo-erythropoietin; APOE, apolipoprotein E; BBB, blood‒brain barrier; BCECs, brain capillary endothelial cells; Blood‒brain barrier; CAT, catalase; COX-1, cyclooxygenase-1; CXCR-4, C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; Ce-NPs, ceria nanoparticles; CsA, cyclosporine A; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; GFs, growth factors; GPIIb/IIIa, glycoprotein IIb/IIIa; HMGB1, high mobility group protein B1; Hb, hemoglobin; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule-1; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; IL-6, interleukin-6; Ischemic cascade; LFA-1, lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1; LHb, liposomal Hb; MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; MSC, mesenchymal stem cell; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; NGF, nerve growth factor; NMDAR, N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor; NOS, nitric oxide synthase; NPs, nanoparticles; NSCs, neural stem cells; Nanomedicine; Neuroprotectant; PBCA, poly-butylcyanoacrylate; PCMS, poly (chloromethylstyrene); PEG, poly-ethylene-glycol; PEG-PLA, poly (ethylene-glycol)-b-poly (lactide); PLGA NPs, poly (l-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles; PSD-95, postsynaptic density protein-95; PSGL-1, P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1; RBCs, red blood cells; RES, reticuloendothelial system; RGD, Arg-Gly-Asp; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Reperfusion; SDF-1, stromal cell-derived factor-1; SHp, stroke homing peptide; SOD, superoxide dismutase; SUR1-TRPM4, sulfonylurea receptor 1-transient receptor potential melastatin-4; Stroke; TEMPO, 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl; TIA, transient ischemic attack; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; Thrombolytics; cRGD, cyclic Arg-Gly-Asp; e-PAM-R, arginine-poly-amidoamine ester; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; miRNAs, microRNAs; nNOS, neuron nitric oxide synthase; siRNA, small interfering RNA.
© 2021 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ameliorating effects of traditional Chinese medicine preparation, Chinese materia medica and active compounds on ischemia/reperfusion-induced cerebral microcirculatory disturbances and neuron damage.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015 Jan;5(1):8-24. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2014.11.002. Epub 2015 Jan 24. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015. PMID: 26579420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracisternal administration of tanshinone IIA-loaded nanoparticles leads to reduced tissue injury and functional deficits in a porcine model of ischemic stroke.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2021 Jan 5;10:18-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2020.11.003. eCollection 2021 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33842909 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomedicine for acute respiratory distress syndrome: The latest application, targeting strategy, and rational design.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Oct;11(10):3060-3091. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.04.023. Epub 2021 May 7. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 33977080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of integrated cancer nanomedicine in overcoming drug resistance.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013 Nov;65(13-14):1784-802. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2013.07.012. Epub 2013 Jul 21. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013. PMID: 23880506 Review.
-
Recent advances in drug delivery systems for targeting cancer stem cells.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Jan;11(1):55-70. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.09.016. Epub 2020 Oct 2. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 33532180 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
M2 Microglia-Derived Exosomes Protect Against Glutamate-Induced HT22 Cell Injury via Exosomal miR-124-3p.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Oct;61(10):7845-7861. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04075-x. Epub 2024 Mar 4. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38433165 Free PMC article.
-
The Recent Applications of PLGA-Based Nanostructures for Ischemic Stroke.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Sep 14;15(9):2322. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15092322. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37765291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carbon Dots Extracted from the Plant Gardenia jasminoides Ameliorates Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jun 11;18(6):870. doi: 10.3390/ph18060870. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573265 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration on the Mechanism of Ubiquitin Proteasome System in Cerebral Stroke.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Apr 7;14:814463. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.814463. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35462700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Size-Dependent Cytoprotective Effects of Selenium Nanoparticles during Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation in Brain Cortical Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 5;23(13):7464. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137464. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Virani S.S., Alonso A., Benjamin E.J., Bittencourt M.S., Callaway C.W., Carson A.P. Heart disease and stroke statistics-‒2020 update: a report from the American heart association. Circulation. 2020;141:e139–e196. - PubMed
-
- Karaszewski B., Wardlaw J.M., Marshall I., Cvoro V., Wartolowska K., Haga K. Early brain temperature elevation and anaerobic metabolism in human acute ischaemic stroke. Brain. 2009;132:955–964. - PubMed
-
- Lewén A., Matz P., Chan P.H. Free radical pathways in CNS injury. J Neurotrauma. 2000;17:871–890. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

