Ginsenosides in Panax genus and their biosynthesis
- PMID: 34386322
- PMCID: PMC8343117
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.12.017
Ginsenosides in Panax genus and their biosynthesis
Abstract
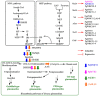
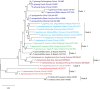
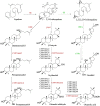
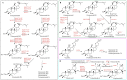
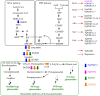
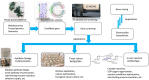
Ginsenosides are a series of glycosylated triterpenoids which belong to protopanaxadiol (PPD)-, protopanaxatriol (PPT)-, ocotillol (OCT)- and oleanane (OA)-type saponins known as active compounds of Panax genus. They are accumulated in plant roots, stems, leaves, and flowers. The content and composition of ginsenosides are varied in different ginseng species, and in different parts of a certain plant. In this review, we summarized the representative saponins structures, their distributions and the contents in nearly 20 Panax species, and updated the biosynthetic pathways of ginsenosides focusing on enzymes responsible for structural diversified ginsenoside biosynthesis. We also emphasized the transcription factors in ginsenoside biosynthesis and non-coding RNAs in the growth of Panax genus plants, and highlighted the current three major biotechnological applications for ginsenosides production. This review covered advances in the past four decades, providing more clues for chemical discrimination and assessment on certain ginseng plants, new perspectives for rational evaluation and utilization of ginseng resource, and potential strategies for production of specific ginsenosides.
Keywords: ABA, abscisic acid; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; AtCPR (ATR), Arabidopsis thaliana cytochrome P450 reductase; BARS, baruol synthase; Biosynthetic pathway; Biotechnological approach; CAS, cycloartenol synthase; CDP, cytidine diphosphate; CPQ, cucurbitadienol synthase; CYP, cytochrome P450; DDS, dammarenediol synthase; DM, dammarenediol-II; DMAPP, dimethylallyl diphosphate; FPP, farnesyl pyrophosphate; FPPS (FPS), farnesyl diphosphate synthase; GDP, guanosine diphosphate; Ginsenoside; HEJA, 2-hydroxyethyl jasmonate; HMGR, HMG-CoA reductase; IPP, isopentenyl diphosphate; ITS, internal transcribed spacer; JA, jasmonic acid; JA-Ile, (+)-7-iso-jasmonoyl-l-isoleucine; JAR, JA-amino acid synthetase; JAZ, jasmonate ZIM-domain; KcMS, Kandelia candel multifunctional triterpene synthases; LAS, lanosterol synthase; LUP, lupeol synthase; MEP, methylerythritol phosphate; MVA, mevalonate; MVD, mevalonate diphosphate decarboxylase; MeJA, methyl jasmonate; NDP, nucleotide diphosphate; Non-coding RNAs; OA, oleanane or oleanic acid; OAS, oleanolic acid synthase; OCT, ocotillol; OSC, oxidosqualene cyclase; PPD, protopanaxadiol; PPDS, PPD synthase; PPT, protopanaxatriol; PPTS, PPT synthase; Panax species; RNAi, RNA interference; SA, salicylic acid; SE (SQE), squalene epoxidase; SPL, squamosa promoter-binding protein-like; SS (SQS), squalene synthase; SUS, sucrose synthase; TDP, thymine diphosphate; Transcription factors; UDP, uridine diphosphate; UGPase, UDP-glucose pyrophosphosphprylase; UGT, UDP-dependent glycosyltransferase; WGD, whole genome duplication; α-AS, α-amyrin synthase; β-AS, β-amyrin synthase.
© 2021 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses revealed the distribution of saponins in Panax notoginseng.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018 May;8(3):458-465. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2017.12.010. Epub 2018 Feb 3. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018. PMID: 29881685 Free PMC article.
-
The Cyt P450 enzyme CYP716A47 catalyzes the formation of protopanaxadiol from dammarenediol-II during ginsenoside biosynthesis in Panax ginseng.Plant Cell Physiol. 2011 Dec;52(12):2062-73. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcr150. Epub 2011 Oct 29. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 22039120
-
Metabolomes and transcriptomes revealed the saponin distribution in root tissues of Panax quinquefolius and Panax notoginseng.J Ginseng Res. 2020 Nov;44(6):757-769. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2019.05.009. Epub 2019 May 29. J Ginseng Res. 2020. PMID: 33192118 Free PMC article.
-
[Research achievements on ginsenosides biosynthesis from Panax ginseng].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016 Dec;41(23):4292-4302. doi: 10.4268/cjcmm20162302. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 28933103 Review. Chinese.
-
Advances in Saponin Diversity of Panax ginseng.Molecules. 2020 Jul 29;25(15):3452. doi: 10.3390/molecules25153452. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32751233 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrative metabolomic and transcriptomic reveals potential mechanism for promotion of ginsenoside synthesis in Panax ginseng leaves under different light intensities.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Nov 22;11:1298501. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1298501. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38076416 Free PMC article.
-
The role of botanical triterpenoids and steroids in bile acid metabolism, transport, and signaling: Pharmacological and toxicological implications.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Aug;14(8):3385-3415. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.04.027. Epub 2024 May 3. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39220868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative transcriptomic analysis provides insights into the regulation of root-specific saponin production in Panax japonicus.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 11;14(1):27572. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78720-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39528625 Free PMC article.
-
The antitumor effects and apoptotic mechanism of 20(S)-Protopanaxadiol in acute myeloid leukemia.J Ginseng Res. 2025 May;49(3):306-314. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2025.03.006. Epub 2025 Mar 20. J Ginseng Res. 2025. PMID: 40453346 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on Effects of Ginsenoside Rg2 and Rh1 on Nervous System and Related Mechanisms.Molecules. 2023 Dec 4;28(23):7935. doi: 10.3390/molecules28237935. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38067664 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee C., Wen J. Phylogeny of Panax using chloroplast trnC-trnD intergenic region and the utility of trnC-trnD in interspecific studies of plants. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2004;31:894–903. - PubMed
-
- Sharma S.K., Pandit M.K. A new species of panax L. (Araliaceae) from Sikkim himalaya, India. Syst Bot. 2009;34:434–438.
-
- Duy N.V., Trieu L.N., Chinh N.D., Tran V.T. A new variety of panax (Araliaceae) from lam vien plateau, vietnam and its molecular evidence. Phytotaxa. 2016;277:47–58.
-
- Pandey A.K., Ali M.A. Intraspecific variation in Panax assamicus Ban. populations based on internal transcribed spacer (ITS) sequences of nrDNA. Indian J Biotechnol. 2012;11:30–38.
-
- Gurung B., Bhardwaj P.K., Rai A.K., Sahoo D. Major ginsenoside contents in rhizomes of Panax sokpayensis and Panax bipinnatifidus. Nat Prod Res. 2018;32:234–238. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

