Anti-inflammatory roles of interleukin-35 in the pathogenesis of Japanese cedar pollinosis
- PMID: 34386410
- PMCID: PMC8331259
- DOI: 10.5415/apallergy.2021.11.e34
Anti-inflammatory roles of interleukin-35 in the pathogenesis of Japanese cedar pollinosis
Abstract
Background: Interleukin (IL)-35 has been recently identified as an anti-inflammatory cytokine in allergic inflammation. However, its biological role in the pathogenesis of allergic rhinitis has not been fully elucidated.
Objective: The purpose of this study was to investigate the anti-inflammatory activity of IL-35 in the pathogenesis of allergic rhinitis in patients with Japanese cedar pollinosis (JCP).
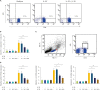
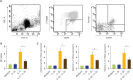
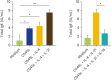
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were collected from healthy controls and JCP patients during the off-season for pollen. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were incubated with Cry j 1, a major allergen of Japanese cedar pollen and production of IL-5, IL-13, and IL-35 were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Th2 (CD4+ST2+) cells and group 2 innate lymphoid cells were isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of JCP patients, and the inhibitory effects of IL-35 on cell differentiation, proliferation and mRNA expression of IL-5, IL-13, and GATA3 were examined. B cells were also isolated and the effects of IL-35 on total IgE production were examined.
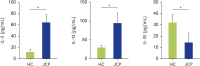
Results: Cry j 1-induced production of IL-5 and IL-13 was significantly increased in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from JCP patients, whereas Cry j 1-induced IL-35 production was significantly decreased compared with healthy controls. IL-35 significantly inhibited Th2 cell differentiation, group 2 innate lymphoid cell proliferation, and mRNA expression of IL-5, IL-13, and GATA3 in Th2 cells and group 2 innate lymphoid cells. IL-35 also inhibited IgE production from B cells.
Conclusion: IL-35 is an important anti-inflammatory cytokine in JCP, and its biological roles include the downregulation of Th2 cells and group 2 innate lymphoid cells, and the inhibition of IgE production from B cells. These findings demonstrate that IL-35 may have the potential to exert anti-allergic effects for the treatment of allergic rhinitis.
Keywords: B cell; Group 2 innate lymphoid cell; IL-35; Japanese cedar pollinosis; Th2 cell.
Copyright © 2021. Asia Pacific Association of Allergy, Asthma and Clinical Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhanced production of IgE anti-Japanese cedar pollen specific antibodies by peripheral blood B cells from patients with Japanese cedar pollinosis.Allergol Int. 2008 Jun;57(2):147-55. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.O-07-510. Allergol Int. 2008. PMID: 18349589
-
Seasonal changes in phytohemagglutinin-induced cytokine synthesis by peripheral blood lymphocytes of patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis due to Japanese cedar pollens.Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1998;538:156-68. doi: 10.1080/00016489850182882. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1998. PMID: 9879416
-
Release of IL-4 and IL-5 from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells co-cultured with Japanese cedar pollen antigen in vitro.Cell Biol Int. 2001;25(8):841-4. doi: 10.1006/cbir.2001.0766. Cell Biol Int. 2001. PMID: 11482911
-
Spectrum of allergens for Japanese cedar pollinosis and impact of component-resolved diagnosis on allergen-specific immunotherapy.Allergol Int. 2015 Oct;64(4):312-20. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2015.05.008. Epub 2015 Jul 3. Allergol Int. 2015. PMID: 26433527 Review.
-
Present situation of cedar pollinosis in Japan and its immune responses.Allergol Int. 2009 Jun;58(2):155-62. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.08-RAI-0074. Epub 2009 Mar 25. Allergol Int. 2009. PMID: 19307773 Review.
Cited by
-
Preface of the Proceedings of the 34rd Workshop on Eosinophils in Allergy and Related Diseases 2020 (WEA 2020).Asia Pac Allergy. 2021 Jul 29;11(3):e36. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2021.11.e36. eCollection 2021 Jul. Asia Pac Allergy. 2021. PMID: 34386412 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Glimpses of the life journey of Prof. Sohei Makino, MD, PhD.Asia Pac Allergy. 2021 Jul 28;11(3):e35. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2021.11.e35. eCollection 2021 Jul. Asia Pac Allergy. 2021. PMID: 34386411 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hu D. Role of anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-35 and IL-37 in asthma. Inflammation. 2017;40:697–707. - PubMed
-
- Choi J, Leung PS, Bowlus C, Gershwin ME. IL-35 and autoimmunity: a comprehensive perspective. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2015;49:327–332. - PubMed
-
- Hunter CA. New IL-12-family members: IL-23 and IL-27, cytokines with divergent functions. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:521–531. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
