Long Non-Coding RNA CCAT2 Promotes the Development of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Inhibiting miR-200b to Upregulate the IGF2BP2/TK1 Axis
- PMID: 34386421
- PMCID: PMC8353391
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.680642
Long Non-Coding RNA CCAT2 Promotes the Development of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Inhibiting miR-200b to Upregulate the IGF2BP2/TK1 Axis
Abstract
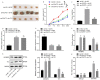
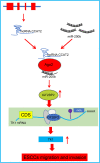
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been shown to play important roles in human cancers, including esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). In the current study, we identified CCAT2 as a relevant lncRNA and investigated its role in the progression of ESCC. RT-qPCR was adopted to detect CCAT2 expression in collected clinical samples, ESCC cell lines, and a normal cell line. We tested the correlation between CCAT2 expression and the prognosis of ESCC. RT-qPCR or immunoblotting was adopted to detect the expression of relevant factors in ESCC tissues or cells. Cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion were examined by colony formation assay, flow cytometry, scratch assay, and Transwell assay, respectively, while subcutaneous tumorigenesis in nude mice was adopted to examine the role of CCAT2 in tumorigenesis of ESCC cells in vivo. Bioinformatics analysis, dual luciferase reporter assay, and RIP were conducted for the target relationship profiling. Me-RIP was adopted to detect m6A modification level of TK1 in ESCC tissues or cells. Upregulated CCAT2, IGF2BP2, and TK1 expression and inhibited miR-200b expression were observed in ESCC cells and tissues. CCAT2 bound to miR-200b and reduced its expression, leading to upregulated IGF2BP2 expression. IGF2BP2 improved TK1 mRNA stability to enhance its expression by recognizing its m6A modification. CCAT2 promoted the migration and invasion of ESCC cells in vitro, and tumorigenesis in vivo by upregulating TK1 expression, while overexpression of miR-200b reversed these effects of CCAT2. Overall, this study suggests that CCAT2 competitively binds to miR-200b to alleviate its inhibitory effects on IGF2BP2 expression, resulting in elevated TK1 expression, and an ensuing promotion of the development of ESCC.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine; competing endogenous RNA; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2; long non-coding RNA CCAT2; microRNA-200b; thymidine kinase 1.
Copyright © 2021 Wu, Fan, Liu, Shen, Lu and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The m6A reader IGF2BP2 promotes the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells by increasing the stability of OCT4 mRNA.Biochem Cell Biol. 2024 Apr 1;102(2):169-178. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2023-0067. Epub 2023 Nov 2. Biochem Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 37917979
-
Knockdown of long non-coding RNA CCAT2 suppresses growth and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting the β-catenin/WISP1 signaling pathway.J Int Med Res. 2021 May;49(5):3000605211019938. doi: 10.1177/03000605211019938. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34057837 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of lncRNAXLOC_001659 inhibits proliferation and invasion of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Nov 14;25(42):6299-6310. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i42.6299. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31754291 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal lncRNA ZFAS1 regulates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation, invasion, migration and apoptosis via microRNA-124/STAT3 axis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Nov 27;38(1):477. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1473-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31775815 Free PMC article.
-
N6-methyladenosine-modified circ_0006168 promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition via miR-384/STAT3/Snail axis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.J Cancer. 2024 Jul 16;15(15):4939-4954. doi: 10.7150/jca.97533. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39132166 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Roles of long non‑coding RNAs in esophageal cell squamous carcinoma (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2024 Aug;54(2):72. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5396. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Int J Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38963019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of RNA N6-methyladenosine in esophageal cancer.Heliyon. 2022 Nov 5;8(11):e11430. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11430. eCollection 2022 Nov. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36387447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Readers of RNA Modification in Cancer and Their Anticancer Inhibitors.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 22;14(7):881. doi: 10.3390/biom14070881. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The implications of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in esophageal carcinoma.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Oct;50(10):8691-8703. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08575-2. Epub 2023 Aug 20. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37598390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The diverse role of RNA methylation in esophageal cancer.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2023 Apr 17;55(6):988-1000. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2023057. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2023. PMID: 37070847 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

