Carbon Nanotubes: A Summary of Beneficial and Dangerous Aspects of an Increasingly Popular Group of Nanomaterials
- PMID: 34386422
- PMCID: PMC8353320
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.693814
Carbon Nanotubes: A Summary of Beneficial and Dangerous Aspects of an Increasingly Popular Group of Nanomaterials
Abstract
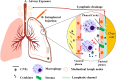
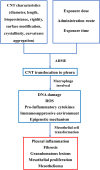
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are nanomaterials with broad applications that are produced on a large scale. Animal experiments have shown that exposure to CNTs, especially one type of multi-walled carbon nanotube, MWCNT-7, can lead to malignant transformation. CNTs have characteristics similar to asbestos (size, shape, and biopersistence) and use the same molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways as those involved in asbestos tumorigenesis. Here, a comprehensive review of the characteristics of carbon nanotubes is provided, as well as insights that may assist in the design and production of safer nanomaterials to limit the hazards of currently used CNTs.
Keywords: asbestos; carbon nanotubes; carcinogen; malignant mesothelioma; nanomaterials.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Wu, de Perrot and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pleural translocation and lesions by pulmonary exposed multi-walled carbon nanotubes.J Toxicol Pathol. 2020 Jul;33(3):145-151. doi: 10.1293/tox.2019-0075. Epub 2020 Mar 13. J Toxicol Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32764839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differences and similarities between carbon nanotubes and asbestos fibers during mesothelial carcinogenesis: shedding light on fiber entry mechanism.Cancer Sci. 2012 Aug;103(8):1378-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2012.02326.x. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Cancer Sci. 2012. PMID: 22568550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genotoxicity and carcinogenicity risk of carbon nanotubes.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013 Dec;65(15):2098-110. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2013.05.011. Epub 2013 Jun 7. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013. PMID: 23751780 Review.
-
The asbestos-carbon nanotube analogy: An update.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2018 Dec 15;361:68-80. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2018.06.027. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29960000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carbon nanotube pathogenicity conforms to a unified theory for mesothelioma causation by elongate materials and fibers.Environ Res. 2023 Aug 1;230:114580. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.114580. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 36965801 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Environmental and Health Implications from the Scaled-Up Production and Disposal of Nanomaterials Used in Biosensors.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 25;12(12):1082. doi: 10.3390/bios12121082. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Mini Review on Electrochemical Nano-biosensors in Detection of Drugs/Pesticides.Indian J Microbiol. 2025 Mar;65(1):216-234. doi: 10.1007/s12088-024-01303-9. Epub 2024 May 28. Indian J Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40371039
-
Pulmonary Toxicity of Long, Thick MWCNT and Very Long, Thin Carboxylated MWCNT Aerosols Following 28 Days Whole-Body Exposure.Toxics. 2025 May 16;13(5):401. doi: 10.3390/toxics13050401. Toxics. 2025. PMID: 40423481 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Insights and Multifactorial Applications of Carbon Nanotubes.Micromachines (Basel). 2021 Nov 30;12(12):1502. doi: 10.3390/mi12121502. Micromachines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34945354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic Value of EMT Gene Signature in Malignant Mesothelioma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 21;24(5):4264. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054264. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901697 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

