ORF3a-Mediated Incomplete Autophagy Facilitates Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 Replication
- PMID: 34386498
- PMCID: PMC8353283
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.716208
ORF3a-Mediated Incomplete Autophagy Facilitates Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 Replication
Abstract
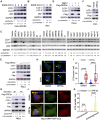
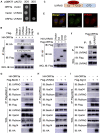
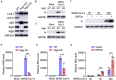
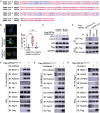
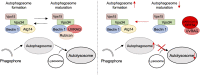
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the causative agent for the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic and there is an urgent need to understand the cellular response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Beclin 1 is an essential scaffold autophagy protein that forms two distinct subcomplexes with modulators Atg14 and UVRAG, responsible for autophagosome formation and maturation, respectively. In the present study, we found that SARS-CoV-2 infection triggers an incomplete autophagy response, elevated autophagosome formation but impaired autophagosome maturation, and declined autophagy by genetic knockout of essential autophagic genes reduces SARS-CoV-2 replication efficiency. By screening 26 viral proteins of SARS-CoV-2, we demonstrated that expression of ORF3a alone is sufficient to induce incomplete autophagy. Mechanistically, SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a interacts with autophagy regulator UVRAG to facilitate PI3KC3-C1 (Beclin-1-Vps34-Atg14) but selectively inhibit PI3KC3-C2 (Beclin-1-Vps34-UVRAG). Interestingly, although SARS-CoV ORF3a shares 72.7% amino acid identity with the SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a, the former had no effect on cellular autophagy response. Thus, our findings provide the mechanistic evidence of possible takeover of host autophagy machinery by ORF3a to facilitate SARS-CoV-2 replication and raise the possibility of targeting the autophagic pathway for the treatment of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; ORF3a; SARS-CoV-2; UVRAG; autophagy.
Copyright © 2021 Qu, Wang, Zhu, Wang, Wang, Hu, Liu, Li, Ren, Xiao, Liu, Wang, Fu, Zhang, Li, Zhang and Liang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a induces RETREG1/FAM134B-dependent reticulophagy and triggers sequential ER stress and inflammatory responses during SARS-CoV-2 infection.Autophagy. 2022 Nov;18(11):2576-2592. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2039992. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Autophagy. 2022. PMID: 35239449 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a inhibits cGAS-STING-mediated autophagy flux and antiviral function.J Med Virol. 2023 Jan;95(1):e28175. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28175. Epub 2022 Oct 8. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 36163413 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of autophagy by SARS-CoV-2: The multifunctional contributions of ORF3a.J Med Virol. 2023 Jul;95(7):e28959. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28959. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 37485696 Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a Induces Incomplete Autophagy via the Unfolded Protein Response.Viruses. 2021 Dec 9;13(12):2467. doi: 10.3390/v13122467. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34960736 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the Role of SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a in Viral Pathogenesis and COVID-19.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 9;13:854567. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.854567. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35356515 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role and clinical implication of autophagy in COVID-19.Virol J. 2023 Jun 16;20(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-02069-0. Virol J. 2023. PMID: 37328875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a-Mediated NF-κB Activation Is Not Dependent on TRAF-Binding Sequence.Viruses. 2023 Nov 8;15(11):2229. doi: 10.3390/v15112229. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38005906 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 viral protein ORF3A injures renal tubules by interacting with TRIM59 to induce STAT3 activation.Mol Ther. 2023 Mar 1;31(3):774-787. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.12.008. Epub 2022 Dec 15. Mol Ther. 2023. PMID: 36523164 Free PMC article.
-
Acute COVID-19 and LongCOVID syndrome - molecular implications for therapeutic strategies - review.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 17;16:1582783. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1582783. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40313948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 ORF3a Viroporin-Influenced Common and Unique Cellular Signaling Cascades in Lung, Heart, and the Brain Choroid Plexus Organoids with Additional Enriched MicroRNA Network Analyses for Lung and the Brain Tissues.ACS Omega. 2023 Nov 17;8(48):45817-45833. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c06485. eCollection 2023 Dec 5. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38075756 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

