Markers of Kidney Injury, Inflammation, and Fibrosis Associated With Ertugliflozin in Patients With CKD and Diabetes
- PMID: 34386658
- PMCID: PMC8343791
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2021.05.022
Markers of Kidney Injury, Inflammation, and Fibrosis Associated With Ertugliflozin in Patients With CKD and Diabetes
Abstract
Introduction: Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors improve cardiovascular and kidney outcomes through mechanisms that are incompletely understood. In this exploratory post-hoc analysis of the VERTIS RENAL trial, we report the association between the SGLT2 inhibitor, ertugliflozin, and markers of kidney injury, inflammation, and fibrosis in participants with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and stage 3 chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Methods: Participants were randomized to ertugliflozin (5 or 15 mg/d) or placebo, and plasma samples for biomarker analysis were collected at baseline, 26 weeks, and 52 weeks.
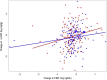
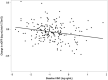
Results: Ertugliflozin-treated participants had lower plasma levels of kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) at 26 weeks (P = 0.044) and 52 weeks (P = 0.007) and higher eotaxin-1 at 52 weeks (P = 0.007) postrandomization compared with placebo. The change in KIM-1 was not associated with the baseline urine albumin to creatinine ratio (UACR) or the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR, P interaction > 0.05). Additionally, the change in KIM-1 was positively correlated with the change in UACR in participants treated with ertugliflozin (P = 0.0071). No other significant associations between ertugliflozin and changes in the markers of tubular injury, inflammation, fibrosis, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction were observed.
Conclusion: In conclusion, in participants with T2D and stage 3 CKD, ertugliflozin was associated with a sustained lowering of the tubular injury marker KIM-1 regardless of baseline kidney function.
Keywords: biomarkers; chronic kidney disease; ertugliflozin; kidney injury molecule-1; sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibition; type 2 diabetes.
© 2021 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Thomas M.C., Cherney D.Z.I. The actions of SGLT2 inhibitors on metabolism, renal function and blood pressure. Diabetologia. 2018;61:2098–2107. - PubMed
-
- Perkovic V., Jardine M.J., Neal B. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2295–2306. - PubMed
-
- Zinman B., Wanner C., Lachin J.M. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2117–2128. - PubMed
-
- Wiviott S.D., Raz I., Bonaca M.P. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:347–357. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

