APOE genotype moderates the relationship between LRP1 polymorphism and cognition across the Alzheimer's disease spectrum via disturbing default mode network
- PMID: 34387022
- PMCID: PMC8504518
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.13716
APOE genotype moderates the relationship between LRP1 polymorphism and cognition across the Alzheimer's disease spectrum via disturbing default mode network
Abstract
Aims: This study aims to investigate the mechanisms by which apolipoprotein E (APOE) genotype modulates the relationship between low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1) rs1799986 variant on the default mode network (DMN) and cognition in Alzheimer's disease (AD) spectrum populations.
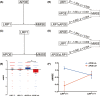
Methods: Cross-sectional 168 subjects of AD spectrum were obtained from Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative database with resting-state fMRI scans and neuropsychological scores data. Multivariable linear regression analysis was adopted to investigate the main effects and interaction of LRP1 and disease on the DMN. Moderation and interactive analyses were performed to assess the relationships among APOE, LRP1, and cognition. A support vector machine model was used to classify AD spectrum with altered connectivity as an objective diagnostic biomarker.
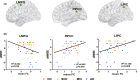
Results: The main effects and interaction of LRP1 and disease were mainly focused on the core hubs of frontal-parietal network. Several brain regions with altered connectivity were correlated with cognitive scores in LRP1-T carriers, but not in non-carriers. APOE regulated the effect of LRP1 on cognitive performance. The functional connectivity of numerous brain regions within LRP1-T carriers yielded strong power for classifying AD spectrum.
Conclusion: These findings suggested LRP1 could affect DMN and provided a stage-dependent neuroimaging biomarker for classifying AD spectrum populations.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; apolipoprotein E; default mode network; low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1.
© 2021 The Authors. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
No authors have any possible conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Harris‐White ME, Frautschy SA. Low density lipoprotein receptor‐related proteins (LRPs), Alzheimer's and cognition. Curr Drug Target CNS Neurol Disord. 2005;4(5):469‐480. - PubMed
-
- Hardy JA, Higgins GA. Alzheimer's disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science. 1992;256(5054):184‐185. - PubMed
-
- Kang DE, Saitoh T, Chen X, et al. Genetic association of the low‐density lipoprotein receptor‐related protein gene (LRP), an apolipoprotein E receptor, with late‐onset Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1997;49(1):56‐61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

