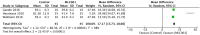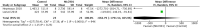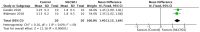Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Efficacy of MLC901 (NeuroAiD IITM) for Acute Ischemic Brain Injury in Animal Models
- PMID: 34387107
- PMCID: PMC8369951
- DOI: 10.1177/2515690X211039219
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Efficacy of MLC901 (NeuroAiD IITM) for Acute Ischemic Brain Injury in Animal Models
Abstract
Introduction: Moleac (MLC) 901 is a traditional Chinese medication approved by the Sino Food and Drug Administration in 2001 for treating stroke. This study aims to analyze the efficacy of MLC901 in animal stroke models after medial cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO).
Methods: Literature selection was performed according to the guidelines of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA) 2015. Inclusion criteria for the experimental studies were the use of animal models, publication in English between 1990 and 2020, information regarding the intervention technique used, and outcomes regarding the efficacy of MLC901 administration.
Results: MLC901 administration resulted in significantly less infarction volume by a mean difference of 17.17 compared to the control group (p < .00001). The MLC901 group resulted in significant improvement in 5-bromo-20-deoxyuridine (BrdU)-positive cells expression by a mean difference of 662.79 (p < .00001) and neurological function, which was indicated by a mean difference in the Bederson Neurological Outcome Score of 1.40 (p < .00001).
Conclusions: MLC901 administration in an animal stroke model resulted in a better reduction in infarction volume and improvement in BrdU expression and neurologic function. These data could help in further determining the efficacy of MLC901 for acute ischemic brain injury in humans.
Keywords: Bederson Neurological Outcome Score; BrdU expression; MLC901; infarction volume; ischemic stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Virani SS, Alonso A, Benjamin EJ, et al.; American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2020 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;141(9):e139–e596. - PubMed
-
- Béjot Y, Bailly H, Durier J, Giroud M. Epidemiology of stroke in Europe and trends for the 21st century. Press Medicale. 2016;45(12):e391–e398. doi:10.1016/j.lpm.2016.10.003 - PubMed
-
- Kusuma Y, Venketasubramanian N, Kiemas LS, Misbach J. Burden of stroke in Indonesia. Int J Stroke. 2009;4(5):379–380. - PubMed
-
- Heurteaux C, Gandin C, Borsotto M, et al.Neuroprotective and neuroproliferative activities of NeuroAid (MLC601, MLC901), a Chinese medicine, in vitro and in vivo. Neuropharmacology. 2010;58(7):987–1001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical