COVID-19 challenges and its therapeutics
- PMID: 34388532
- PMCID: PMC8339548
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112015
COVID-19 challenges and its therapeutics
Abstract
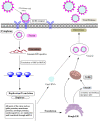
COVID-19, an infectious disease, has emerged as one of the leading causes of death worldwide, making it one of the severe public health issues in recent decades. nCoV, the novel SARS coronavirus that causes COVID-19, has brought together scientists in the quest for possible therapeutic and preventive measures. The development of new drugs to manage COVID-19 effectively is a challenging and time-consuming process, thus encouraging extensive investigation of drug repurposing and repositioning candidates. Several medications, including remdesivir, hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine, lopinavir, favipiravir, ribavirin, ritonavir, interferons, azithromycin, capivasertib and bevacizumab, are currently under clinical trials for COVID-19. In addition, several medicinal plants with considerable antiviral activities are potential therapeutic candidates for COVID-19. Statistical data show that the pandemic is yet to slow down, and authorities are placing their hopes on vaccines. Within a short period, four types of vaccines, namely, whole virus, viral vector, protein subunit, and nucleic acid (RNA/DNA), which can confer protection against COVID-19 in different ways, were already in a clinical trial. SARS-CoV-2 variants spread is associated with antibody escape from the virus Spike epitopes, which has grave concerns for viral re-infection and even compromises the effectiveness of the vaccines. Despite these efforts, COVID-19 treatment is still solely based on clinical management through supportive care. We aim to highlight the recent trends in COVID-19, relevant statistics, and clinical findings, as well as potential therapeutics, including in-line treatment methods, preventive measures, and vaccines to combat the prevalence of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; NCoV; Pneumonia; Prevention; Treatment; Vaccines.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Masson SAS.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Comber L., Walsh K.A., Jordan K., O’Brien K.K., Clyne B., Teljeur C., Drummond L., Carty P.G., De Gascun C.F., Smith S.M. Alternative clinical specimens for the detection of SARS-CoV-2: a rapid review. Rev. Med. Virol. 2021;31:2185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

