An artifıcial ıntelligence approach to automatic tooth detection and numbering in panoramic radiographs
- PMID: 34388975
- PMCID: PMC8361658
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-021-00656-7
An artifıcial ıntelligence approach to automatic tooth detection and numbering in panoramic radiographs
Abstract
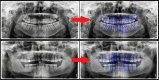
Background: Panoramic radiography is an imaging method for displaying maxillary and mandibular teeth together with their supporting structures. Panoramic radiography is frequently used in dental imaging due to its relatively low radiation dose, short imaging time, and low burden to the patient. We verified the diagnostic performance of an artificial intelligence (AI) system based on a deep convolutional neural network method to detect and number teeth on panoramic radiographs.
Methods: The data set included 2482 anonymized panoramic radiographs from adults from the archive of Eskisehir Osmangazi University, Faculty of Dentistry, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology. A Faster R-CNN Inception v2 model was used to develop an AI algorithm (CranioCatch, Eskisehir, Turkey) to automatically detect and number teeth on panoramic radiographs. Human observation and AI methods were compared on a test data set consisting of 249 panoramic radiographs. True positive, false positive, and false negative rates were calculated for each quadrant of the jaws. The sensitivity, precision, and F-measure values were estimated using a confusion matrix.
Results: The total numbers of true positive, false positive, and false negative results were 6940, 250, and 320 for all quadrants, respectively. Consequently, the estimated sensitivity, precision, and F-measure were 0.9559, 0.9652, and 0.9606, respectively.
Conclusions: The deep convolutional neural network system was successful in detecting and numbering teeth. Clinicians can use AI systems to detect and number teeth on panoramic radiographs, which may eventually replace evaluation by human observers and support decision making.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Deep learning; Panoramic radiography; Tooth.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
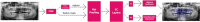

References
-
- Angelopoulos C, Bedard A, Katz JO, Karamanis S, Parissis N. Digital panoramic radiography: an overview. Semin. Orthod. 2004;10:194–203. doi: 10.1053/j.sodo.2004.05.003. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

