Straglr: discovering and genotyping tandem repeat expansions using whole genome long-read sequences
- PMID: 34389037
- PMCID: PMC8361843
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-021-02447-3
Straglr: discovering and genotyping tandem repeat expansions using whole genome long-read sequences
Abstract
Tandem repeat (TR) expansion is the underlying cause of over 40 neurological disorders. Long-read sequencing offers an exciting avenue over conventional technologies for detecting TR expansions. Here, we present Straglr, a robust software tool for both targeted genotyping and novel expansion detection from long-read alignments. We benchmark Straglr using various simulations, targeted genotyping data of cell lines carrying expansions of known diseases, and whole genome sequencing data with chromosome-scale assembly. Our results suggest that Straglr may be useful for investigating disease-associated TR expansions using long-read sequencing.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
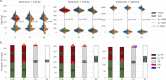
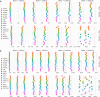
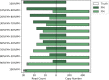
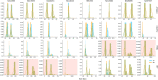
References
-
- Shafin K, Pesout T, Lorig-Roach R, Haukness M, Olsen HE, Bosworth C, Armstrong J, Tigyi K, Maurer N, Koren S, Sedlazeck FJ, Marschall T, Mayes S, Costa V, Zook JM, Liu KJ, Kilburn D, Sorensen M, Munson KM, Vollger MR, Monlong J, Garrison E, Eichler EE, Salama S, Haussler D, Green RE, Akeson M, Phillippy A, Miga KH, Carnevali P, Jain M, Paten B. Nanopore sequencing and the Shasta toolkit enable efficient de novo assembly of eleven human genomes. Nat Biotechnol. 2020;38(9):1044–1053. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0503-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wenger AM, Peluso P, Rowell WJ, Chang PC, Hall RJ, Concepcion GT, Ebler J, Fungtammasan A, Kolesnikov A, Olson ND, Töpfer A, Alonge M, Mahmoud M, Qian Y, Chin CS, Phillippy AM, Schatz MC, Myers G, DePristo MA, Ruan J, Marschall T, Sedlazeck FJ, Zook JM, Li H, Koren S, Carroll A, Rank DR, Hunkapiller MW. Accurate circular consensus long-read sequencing improves variant detection and assembly of a human genome. Nat Biotechnol. 2019;37(10):1155–1162. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0217-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

