First-in-human phase I/Ib open-label dose-escalation study of GWN323 (anti-GITR) as a single agent and in combination with spartalizumab (anti-PD-1) in patients with advanced solid tumors and lymphomas
- PMID: 34389618
- PMCID: PMC8365809
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002863
First-in-human phase I/Ib open-label dose-escalation study of GWN323 (anti-GITR) as a single agent and in combination with spartalizumab (anti-PD-1) in patients with advanced solid tumors and lymphomas
Abstract
Background: GWN323 is an IgG1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) against the glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor-related protein. This first-in-human, open-label phase I/Ib study aimed to investigate the safety and tolerability and to identify the recommended doses of GWN323 with/without spartalizumab, an anti-programmed cell death receptor-1 agent, for future studies. Pharmacokinetics, preliminary efficacy and efficacy biomarkers were also assessed.
Methods: Patients (aged ≥18 years) with advanced/metastatic solid tumors with Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of ≤2 were included. GWN323 (10-1500 mg) or GWN323+spartalizumab (GWN323 10-750 mg+spartalizumab 100-300 mg) were administered intravenously at various dose levels and schedules during the dose-escalation phase. Dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) were assessed during the first 21 days in a single-agent arm and 42 days in a combination arm. Adverse events (AEs) were graded per National Cancer Institute-Common Toxicity Criteria for Adverse Events V.4.03 and efficacy was assessed using Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors V.1.1.
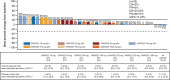
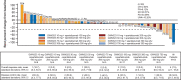
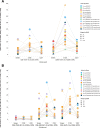
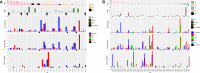
Results: Overall, 92 patients (single-agent, n=39; combination, n=53) were included. The maximum administered doses (MADs) in the single-agent and combination arms were GWN323 1500 mg every 3 weeks (q3w) and GWN323 750 mg+spartalizumab 300 mg q3w, respectively. No DLTs were observed with single-agent treatment. Three DLTs (6%, all grade ≥3) were noted with combination treatment: blood creatine phosphokinase increase, respiratory failure and small intestinal obstruction. Serious AEs were reported in 30.8% and 34.0%, and drug-related AEs were reported in 82.1% and 77.4% of patients with single-agent and combination treatments, respectively. Disease was stable in 7 patients and progressed in 26 patients with single-agent treatment. In combination arm patients, 1 had complete response (endometrial cancer); 3, partial response (rectal cancer, adenocarcinoma of colon and melanoma); 14, stable disease; and 27, disease progression. GWN323 exhibited a pharmacokinetic profile typical of mAbs with a dose-dependent increase in the pharmacokinetic exposure. Inconsistent decreases in regulatory T cells and increases in CD8+ T cells were observed in the combination arm. Gene expression analyses showed no significant effect of GWN323 on interferon-γ or natural killer-cell signatures.
Conclusions: GWN323, as a single agent and in combination, was well tolerated in patients with relapsed/refractory solid tumors. The MAD was 1500 mg q3w for single-agent and GWN323 750 mg+spartalizumab 300 mg q3w for combination treatments. Minimal single-agent activity and modest clinical benefit were observed with the spartalizumab combination.
Trial registration number: NCT02740270.
Keywords: antibodies; clinical trials as topic; combination; drug therapy; investigational; neoplasm; therapies.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: SAP-P reports other from AbbVie, Inc., other from ABM Therapeutics, Inc., other from Acepodia, Inc., other from Alkermes, other from Aminex Therapeutics, other from Amphivena Therapeutics, Inc., other from BioMarin Pharmaceutical, Inc., other from Boehringer Ingelheim, other from Bristol Myers Squib, other from Cerulean Pharma, Inc., other from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., other from Curis, Inc., other from Daiichi Sankyo, Inc., other from Eli Lilly, other from ENB Therapeutics, other from Five Prime Therapeutics, other from Gene Quantum, other from Genmab A/S, other from GlaxoSmithKline, other from Helix BioPharma Corp., other from Incyte Corp., other from Jacobio Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd., other from Medimmune, LLC., other from Medivation, Inc., other from Merck Sharp and Dohme Corp., other from Novartis Pharmaceuticals, other from Pieris Pharmaceuticals, Inc., other from Pfizer, other from Principia Biopharma, Inc., other from Puma Biotechnology, Inc., other from Rapt Therapeutics, Inc., other from Seattle Genetics, other from Silverback Therapeutics, other from Taiho Oncology, other from Tesaro, Inc., other from TransThera Bio, grants from NCI/NIH P30CA016672 - Core Grant (CCSG Shared Resources) outside the submitted work. RG reports honoraria (self) from BMS, Lilly, Medison, Roche, Novartis, Janssen, Takeda, MSD, Pfizer, Merck; advisory/consultancy to EISAI, AstraZeneca, Bayer, MSD, Novartis, BI. BOL Pharma, Roche; research grant/funding (institution): educational grant to the research unit—Novartis; travel/accommodations/expenses: Merck, Bayer, BMS, Medison. TT reports grants, personal fees and non-financial support from AstraZeneca; personal fees from Roche, Novartis, Pfizer, DKSH Singapore; other from Immunomedics, outside the submitted work. DWTL reports grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb; personal fees from MSD, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Pfizer; non-financial support from Astra-Zeneca, outside the submitted work. CH reports grants from Merck; personal fees from MSD, Lilly, and Merck, outside the submitted work. TD reports grants from Lilly, Merck Serono, Pfizer, Quintiles (IQVIA), and Eisai; grants and personal fees from MSD, Daiichi Sankyo, Sumitomo Dainippon, Taiho, Novartis, Janssen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Abbvie; personal fees from Amgen, Takeda, Chugai Pharma, Bayer, Rakuten Medical, Ono Pharmaceutical, Astellas Pharma, Oncolys BioPharma, Otsuka Pharma, outside the submitted work. OR reports personal fees from Imvax, GSK, Bayer, Gennentech, Sobi, Puretech, Maverick Therapeutics, Merck, outside the submitted work. In addition, OR has patent methods of using pembrolizumab and trebananib pending. AL reports grants from Novartis, during the conduct of the study; grants from Bristol Myers Squib, personal fees from Trillium Therapeutics, grants, personal fees and non-financial support from Pfizer, grants and personal fees from Janssen, outside the submitted work. In addition, AL has a patent US20150037346A1 with royalties paid. JL reports Scientific Advisory Board: (no stock) 7 Hills, Spring bank (stock) Actym, Alphamab Oncology, Arch Oncology, Kanaph, Mavu, Onc.AI, Pyxis, Tempest; Consultancy with compensation: Abbvie, Alnylam, Array, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Checkmate, Cstone, Eisai, EMD Serono, KSQ, Janssen, Inzen, Macrogenics, Merck, Mersana, Nektar, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Ribon, Rubius, Silicon, Synlogic, TRex, Werewolf, Xilio, Xencor; Research Support: (all to institution for clinical trials unless noted) AbbVie, Agios (IIT), Array (IIT), Astellas, Bristol-Myers Squibb (IIT & industry), Corvus, EMD Serono, Immatics, Incyte, Kadmon, Macrogenics, Merck, Moderna, Nektar, Numab, Replimmune, Rubius, Spring bank, Synlogic, Takeda, Trishula, Tizona, Xencor; Patents: (both provisional) Serial #15/612,657 (Cancer Immunotherapy), PCT/US18/36052 (Microbiome Biomarkers for Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Responsiveness: Diagnostic, Prognostic and Therapeutic Uses Thereof). JO is a full-time employee and stockholder of Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp. LN, AS, AX, XC and JM are full-time employees and stockholders of Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp. PLB reports grants from Novartis, during the conduct of the study; grants from BristolMyersSquibb, grants from Sanofi, grants from Genentech/Roche, grants from Novartis, grants from GlaxoSmithKline, grants from Nektar Therapeutics, grants from Merck, grants from Lilly, grants from Servier, grants from PTC Therapeutics, grants from SeaGen, grants from Sanofi, grants from Mersana, grants from Amgen, grants from Zymeworks, grants from VelosBio, outside the submitted work; and uncompensated advisory boards for BristolMyersSquibb, Sanofi, Pfizer, Genentech/Roche, Amgen, Lilly, SeaGen, Merck; Past Chair, Investigational New Drug Committee, Canadian Clinical Trials Group; executive board member, Breast International Group; steering committee member, American Association for Cancer Research Project GENIE; member, NCI-BIO Breast Cancer Immunotherapy Task Force; Interface Committee, Alexandria Phase III Trial.
Figures
Similar articles
-
First-in-human phase I/Ib study of NIZ985, a recombinant heterodimer of IL-15 and IL-15Rα, as a single agent and in combination with spartalizumab in patients with advanced and metastatic solid tumors.J Immunother Cancer. 2023 Oct;11(10):e007725. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-007725. J Immunother Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37907221 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
First-in-human study of FAZ053, an anti-programmed death-ligand 1 (anti-PD-L1) monoclonal antibody, alone and in combination with spartalizumab (anti-PD-1), in patients with advanced malignancies.ESMO Open. 2025 Jun;10(6):105051. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2025.105051. Epub 2025 May 16. ESMO Open. 2025. PMID: 40381383 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A first-in-human phase 1 dose escalation study of spartalizumab (PDR001), an anti-PD-1 antibody, in patients with advanced solid tumors.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Mar;8(1):e000530. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000530. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32179633 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Rituximab: a review of its use in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.Drugs. 2003;63(8):803-43. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00005. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12662126 Review.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitor-based combinations: is dose escalation mandatory for phase I trials?Ann Oncol. 2019 Nov 1;30(11):1751-1759. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz286. Ann Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31435659 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterizing and correcting immune dysfunction in non-tuberculous mycobacterial disease.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 10;13:1047781. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1047781. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36439147 Free PMC article.
-
Current trends in sensitizing immune checkpoint inhibitors for cancer treatment.Mol Cancer. 2024 Dec 26;23(1):279. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02179-5. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39725966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The nexus of dynamic T cell states and immune checkpoint blockade therapy in the periphery and tumor microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 10;14:1267918. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1267918. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37881432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination strategies with PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: current advances and future directions.Mol Cancer. 2022 Jan 21;21(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01489-2. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35062949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phase I/II study of BMS-986156 with ipilimumab or nivolumab with or without stereotactic ablative radiotherapy in patients with advanced solid malignancies.J Immunother Cancer. 2024 Oct 9;12(10):e009975. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-009975. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39384194 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
